Lab Values Reference Guide: Normal Ranges & Interpretation
advertisement

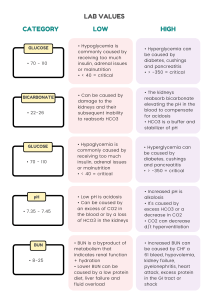
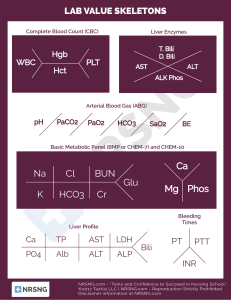
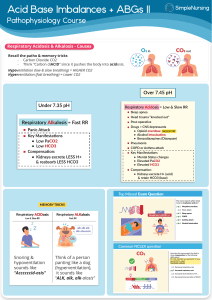
LAB VALUES CATEGORY GLUCOSE • 70 - 110 BICARBONATE • 22-26 GLUCOSE • 70 - 110 pH • 7.35 - 7.45 BUN • 8-25 LOW • Hypoglycemia is commonly caused by receiving too much insulin, adrenal issues or malnutrition • < 40 = critical • Can be caused by damage to the kidneys and their subsequent inability to reabsorb HCO3 HIGH • Hyperglycemia can be caused by diabetes, cushings and pancreatitis • > -350 = critical • The kidneys reabsorb bicarbonate elevating the pH in the blood to compensate for acidosis • HCO3 is a buffer and stabilizer of pH • Hypoglycemia is commonly caused by receiving too much insulin, adrenal issues or malnutrition • < 40 = critical • Hyperglycemia can be caused by diabetes, cushings and pancreatitis • > -350 = critical • Low pH is acidosis • Can be caused by an excess of CO2 in the blood or by a loss of HCO3 in the kidneys • Increased pH is alkalosis • It's caused by excess HCO3 or a decrease in CO2 • CO2 can decrease d/t hyperventilation • BUN is a byproduct of metabolism that indicates renal function + hydration • Lower BUN can be caused by a low protein diet, liver failure and fluid overload • Increased BUN can be caused by CHF a 61 bleed, hypovolemia, kidney failure, pyelonephritis, heart attack, excess protein in the GI tract or shock CATEGORY GLUCOSE • 70 - 110 BICARBONATE • 22-26 GLUCOSE • 70 - 110 pH • 7.35 - 7.45 BUN • 8-25 LOW • Hypoglycemia is commonly caused by receiving too much insulin, adrenal issues or malnutrition • < 40 = critical • Can be caused by damage to the kidneys and their subsequent inability to reabsorb HCO3 HIGH • Hyperglycemia can be caused by diabetes, cushings and pancreatitis • > -350 = critical • The kidneys reabsorb bicarbonate elevating the pH in the blood to compensate for acidosis • HCO3 is a buffer and stabilizer of pH • Hypoglycemia is commonly caused by receiving too much insulin, adrenal issues or malnutrition • < 40 = critical • Hyperglycemia can be caused by diabetes, cushings and pancreatitis • > -350 = critical • Low pH is acidosis • Can be caused by an excess of CO2 in the blood or by a loss of HCO3 in the kidneys • Increased pH is alkalosis • It's caused by excess HCO3 or a decrease in CO2 • CO2 can decrease d/t hyperventilation • BUN is a byproduct of metabolism that indicates renal function + hydration • Lower BUN can be caused by a low protein diet, liver failure and fluid overload • Increased BUN can be caused by CHF a 61 bleed, hypovolemia, kidney failure, pyelonephritis, heart attack, excess protein in the GI tract or shock CATEGORY CREATININE • 0.6-1.5 HEMOGLOBIN • Male: 13-18% • Female: 12-16% HEMATOCRIT • Male: 13-18% • Female: 12-16% PLATELET • 150k-350k WBC • 4300-10800 LOW HIGH • Lower creatinine can be cause by spinal cord injuries or abrupt decreases in movements as it is also byproduct of metabolism creatinine is excreted by the kidney • Can indicate kidney failure, dehydration, rhabdomyolysis, hyperthyroidism, muscular dystrophy, or an obstructed urinary tract • Low Hgb is usually caused by blood loss, anemia, bone marrow, suppression, leukemia and renal problems • Can be caused by living in high altitude, long term smoking, tumors, polycythemia vera and erythropoietin use • Higher hematocrit can be due to over dehydration, blood loss, chemo and lead poisoning • Hematocrit usually directly correlates to hemoglobin and should be 3xHgb • Low platelets put the patient at a very high risk for bleeding and can be caused DIC, aplastic anemia • Increased platelet can be caused by myelogenous leukemia, recent spleen removal, inflammation • Neutropenia is usually caused by bone marrow deficiency, chemo drugs, viral disease, splenic deficiency and radiation • Infection, leukemia, inflammatory diseases and stress can all cause an increased WBC count CATEGORY ALT • 13-69 LOW HIGH • Low ALT is expected and shows normal liver function • High levels of ALT can an early indicator of liver disease. • It is more specific of a test that AST • Low levels of AST in the blood are expected and normal • High levels of AST can indicate chronic-acute hepatitis cirrhosis and other liver disorders • Because the liver produces albumin, low albumin usually means liver damage or cirrhosis • Albumin can also be low in burns due to third spacing • Dehydration can cause high albumin result due to less water in the blood • A decrease in total protein can be caused by liver disease, hemorrhaging, diarrhea and vomiting • High total protein can be seen with chronic inflammation, bone marrow disorders, hepatitis or HIV AST • 5-40 ALBUMIN • 3.4-5.0 TOTAL PROTEIN • 6.4 - 8.0 OTHER LAB VALUES Vital Signs • Blood Pressure - Systolic: 120 mmHg - Diastolic: 80 mmHg • Heart Rate: 60-100 BPM • Respirations: 12 - 20 Breaths / Minute • Oxygen: 95 - 100% • Temperature: 97.8 - 99°F Vital Signs Renal • Calcium: 9 - 11 mg/dL • Magnesium: 1.5 - 2.5 mg/dL • Specific gravity: 1.010 - 1.030 • Phosphorus: 2.5 - 4.5 mg/dL • GFR: 90 - 120 mL/min ABG's • PaCO3: 35 - 45 mmHg • PaO2: 80 - 100 mmHg • HCO3: 22 - 26 mEq/L Pancreas • Amylase: 30 - 110 U/L • Lipase: 0 - 150 U/L COAGs • PT: 10 - 13 sec • PTT: 25 - 35 sec • aPTT: 30 - 40 sec (heparin) • INR - NOT ON Warfarin < 1 sec - ON Warfarin 2 to 3 sec Basal Metabolic Panel (BMP) • Sodium: 135 - 145 mEq/L • Potassium: 3.5 - 5.0 mEq/L • Chloride: 95 - 105 mEq/L • Calcium: 9 - 11 mg/dL • Albumin: 3.4 - 5.4 g/dL • Total protein: 6.2 - 8.2 g/dL Liver Function Test (LFT) • ALP: 40- 120 U/L • Bilirubin: 0.1 - 1.2 mg/dL Lipid Panel • Total Cholesterol: <200 mg/dL • Triglyceride: <150 mg/dL • LDL: <100 mg/dL (Bad Cholesterol) • HDL: >60 mg/dL (Good Cholesterol) HbA1c • Non-diabetic: 4 - 5.6% • Pre-diabetic: 5.7 - 6.4% • Diabetic: >6.5% Complete Blood Count (CBC) • WBC: 4500 - 11000 / µL • RBC: 4.5 – 5.5 million/µL • PLT: 150000 - 450000/µL Others... • MAP: 70 - 100 mmHg • ICP (Intracranial Pressure): 5 - 15 mmHg • BMI: 18.5 - 24.9 • Glascow coma scale: - Best: 15 - Mild: 13 - 15 Measured Therapeutic Antidote - Moderate: 9 - 12 with Range - Severe: 3 - 8 Protamine Heparin aPTT 1.5 - 2.0 x normal Sulfate "control" value Warfarin INR 1.5 - 2.0 x normal Vitamin K "control" value ARTERIAL BLOOD GAS INTERPRETATION • Know your Laboratory Values Acidosis Therapeuti c Range Antidote pH <7.35 7.35 - 7.45 >7.45 CO2 >45 35-45 <35 HCO3 <22 22-26 >26 • Determine if it is a respiratory or metabolic problem Alkalosis • Respiratory - pH is high and CO2 is low • Metabolic - pH is high and HCO3 is high Acidosis • Opposite - pH is low and CO2 is high • Equal - pH is low and HCO3 is low • Determine if it is an uncompensated, partially compensated, or fully compensated • Uncompensated: If the pH is out of range & CO2 or HCO3 is in range • Partially Compensated: If CO2 & HCO3 are both out of range & the pH is out of range • Fully Compensated: If pH is in range (7.35 - 7.45) LABORATORY VALUES MEMORY TRICKS Potassium (3.5-5) • Bananas: -There are about 3-5 in every bunch and you want them half ripe (1/2) So think 3.5 - 5.0 Phosphorus (2.5-4.5) • Phos: 4 letters • Us: 2 (me + you = 2) Don't forget about the .5 Calcium (9-11) • Just call 911!!! Magnesium (1.5-2.5) • Magnifying glass you see 1.5-2.5 bigger than normal. WOW! It looks BIG!!! Chloride (95-105) • Think of a chlorinated pool that you want to go in when it's SUPER HOT!: 95-905°F BUN (7-20mg/dL) • Think of hamburger BUNs... Hamburgers can cost anywhere from 7$ - 20$ Creatine (0.6-1.2mg/dL) • This is the same value as LITHIUM's therapeutic range (0.6-1.2 mmol/L) Lithium is excreted almost solely by the kidneys and creatine is a value that tests how well your kidneys filter Sodium (135-145) • Use the letters “od” in sodium to remember “odd” numbers. • The first 3 odd numbers are 1, 3, and 5 add 10 135 + 10 = 145 Glucose (70-100 mg/dL) • Energy gets low at the age of 70-100 AST (9-40 U/L) • (AST) School = 9AM - 4PM ALT (7-60 U/L) • (ALT) Labor = 7AM - 6PM