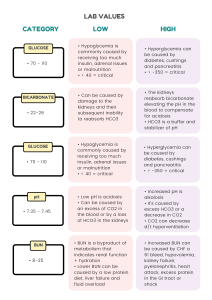
LAB VALUES CATEGORY GLUCOSE • 70 - 110 BICARBONATE • 22-26 GLUCOSE • 70 - 110 pH • 7.35 - 7.45 BUN • 8-25 LOW • Hypoglycemia is commonly caused by receiving too much insulin, adrenal issues or malnutrition • < 40 = critical • Can be caused by damage to the kidneys and their subsequent inability to reabsorb HCO3 HIGH • Hyperglycemia can be caused by diabetes, cushings and pancreatitis • > -350 = critical • The kidneys reabsorb bicarbonate elevating the pH in the blood to compensate for acidosis • HCO3 is a buffer and stabilizer of pH • Hypoglycemia is commonly caused by receiving too much insulin, adrenal issues or malnutrition • < 40 = critical • Hyperglycemia can be caused by diabetes, cushings and pancreatitis • > -350 = critical • Low pH is acidosis • Can be caused by an excess of CO2 in the blood or by a loss of HCO3 in the kidneys • Increased pH is alkalosis • It's caused by excess HCO3 or a decrease in CO2 • CO2 can decrease d/t hyperventilation • BUN is a byproduct of metabolism that indicates renal function + hydration • Lower BUN can be caused by a low protein diet, liver failure and fluid overload • Increased BUN can be caused by CHF a 61 bleed, hypovolemia, kidney failure, pyelonephritis, heart attack, excess protein in the GI tract or shock CATEGORY GLUCOSE • 70 - 110 BICARBONATE • 22-26 GLUCOSE • 70 - 110 pH • 7.35 - 7.45 BUN • 8-25 LOW • Hypoglycemia is commonly caused by receiving too much insulin, adrenal issues or malnutrition • < 40 = critical • Can be caused by damage to the kidneys and their subsequent inability to reabsorb HCO3 HIGH • Hyperglycemia can be caused by diabetes, cushings and pancreatitis • > -350 = critical • The kidneys reabsorb bicarbonate elevating the pH in the blood to compensate for acidosis • HCO3 is a buffer and stabilizer of pH • Hypoglycemia is commonly caused by receiving too much insulin, adrenal issues or malnutrition • < 40 = critical • Hyperglycemia can be caused by diabetes, cushings and pancreatitis • > -350 = critical • Low pH is acidosis • Can be caused by an excess of CO2 in the blood or by a loss of HCO3 in the kidneys • Increased pH is alkalosis • It's caused by excess HCO3 or a decrease in CO2 • CO2 can decrease d/t hyperventilation • BUN is a byproduct of metabolism that indicates renal function + hydration • Lower BUN can be caused by a low protein diet, liver failure and fluid overload • Increased BUN can be caused by CHF a 61 bleed, hypovolemia, kidney failure, pyelonephritis, heart attack, excess protein in the GI tract or shock CATEGORY CREATININE • 0.6-1.5 HEMOGLOBIN • Male: 13-18% • Female: 12-16% HEMATOCRIT • Male: 13-18% • Female: 12-16% PLATELET • 150k-350k WBC • 4300-10800 LOW HIGH • Lower creatinine can be cause by spinal cord injuries or abrupt decreases in movements as it is also byproduct of metabolism creatinine is excreted by the kidney • Can indicate kidney failure, dehydration, rhabdomyolysis, hyperthyroidism, muscular dystrophy, or an obstructed urinary tract • Low Hgb is usually caused by blood loss, anemia, bone marrow, suppression, leukemia and renal problems • Can be caused by living in high altitude, long term smoking, tumors, polycythemia vera and erythropoietin use • Higher hematocrit can be due to over dehydration, blood loss, chemo and lead poisoning • Hematocrit usually directly correlates to hemoglobin and should be 3xHgb • Low platelets put the patient at a very high risk for bleeding and can be caused DIC, aplastic anemia • Increased platelet can be caused by myelogenous leukemia, recent spleen removal, inflammation • Neutropenia is usually caused by bone marrow deficiency, chemo drugs, viral disease, splenic deficiency and radiation • Infection, leukemia, inflammatory diseases and stress can all cause an increased WBC count CATEGORY ALT • 13-69 LOW HIGH • Low ALT is expected and shows normal liver function • High levels of ALT can an early indicator of liver disease. • It is more specific of a test that AST • Low levels of AST in the blood are expected and normal • High levels of AST can indicate chronic-acute hepatitis cirrhosis and other liver disorders • Because the liver produces albumin, low albumin usually means liver damage or cirrhosis • Albumin can also be low in burns due to third spacing • Dehydration can cause high albumin result due to less water in the blood • A decrease in total protein can be caused by liver disease, hemorrhaging, diarrhea and vomiting • High total protein can be seen with chronic inflammation, bone marrow disorders, hepatitis or HIV AST • 5-40 ALBUMIN • 3.4-5.0 TOTAL PROTEIN • 6.4 - 8.0