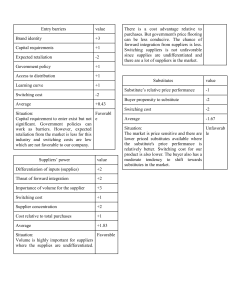
Industry Analysis • Identification of industry’s profit potential • Five Forces Model Threat of entry. Power of suppliers Power of buyers. Threat of substitutes. Rivalry among existing competitors Threat of Entry • Economies of Scale • Network Effects • Customer Switching Costs • Capital Requirements • Advantages Independent of Size • Government Policy Power of Suppliers ( Low) • M-Link • Ring • Backward Integration • Suppliers owned by Parent Company Power of buyers (High) • Low Switching Cost • Standardized or Undifferentiated Product • Threat of Substitutes (High) • Substitute offers an attractive price-performance trade-off • The buyer’s cost of switching to the substitute is low Rivalry among existing competitors (High) • Competitive industry structure The number and size of its competitors. The firms’ degree of pricing power. The type of product or service. The height of entry barriers • Industry growth. • Strategic commitments. • Exit barriers.