External Analysis in Business: SWOT, Environment, Porter's 5 Forces
advertisement

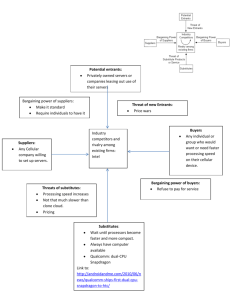
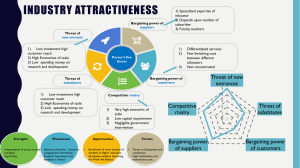
HIH Ch. 2 – External Analyses How does external analysis affect a business' ability to discern strategic opportunities and threats during a SWOT analysis? For a company to have properly conducted a SWOT analysis and identified strategic opportunities and threats an external analysis is essential. It helps in identifying market trends, consumer wants/needs, rival strategies, and governmental developments. Businesses can identify possibilities for growth and eliminate risks by comprehending the external forces. It offers contextual knowledge, aids decision-making, and enables companies to forecast and assess to market developments. The ability of a corporation to match its internal resources with external opportunities and dangers is improved by external analysis, which supports strategic decision-making. Discuss the elements/factors of the General Environment and how trends and changes in each affects the strategy and performance of businesses. The general environment is composed of seven environmental segments that influence the industry and the firms within them. The changes and trends within these segments influence the business’s strategy and performance. Their are two environments that separate these seven segments known as the industry environment and the competitor environment. The industry environment is a set of four factors that directly pertain to the influence of the firm and its competitive actions and responses (the threat of new entrants, the power of suppli- ers, the power of buyers, the threat of product substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry). Industry Environment: 1. Demographic Segment: Population size, age structure, geographic distribution, ethnic mix, and income distribution. 2. Economic Segment: the character and direction of the market that a company competes in or might compete in. 3. Sustainable Physical Segment: potential and actual changes in the physical environment and business practices that are intended to positively respond to those changes in order to create a sustainable environment 4. Sociocultural Segment: concern of society’s attitudes and cultural values. As attitudes and values form a society, this is what will drive demographic, economic, political/legal, and technological conditions and changes. Competitor Environment: 5. Political / Legal Segment: arena in which organizations and interest groups compete for attention, resources, and a voice in overseeing the body of laws and regulations guiding interactions among nations as well as between firms and various local governmental agencies. 6. Technological Segment: the institutions and activities involved in creating new knowledge and translating that knowledge into new outputs, products, processes, and materials. 7. Global Segment: relevant new global markets and their critical cultural and institutional characteristics, existing markets that are changing, and important international political events. Trends and changes in each of these elements of the general environment can significantly impact a company's strategy and performance. Businesses can spot new opportunities, risks, and adjust their strategy as necessary by closely monitoring and analyzing these aspects. Environmental changes can be caused by having missed opportunities, competitive disadvantages, or even economic disruptions if they are not acknowledged and addressed. The long term success of a business requires a hyper awareness to the overall environment and how it affects business. What are Porter's Five Forces, and how are they used to analyze an industry? Choose an industry in which you are interested, and use this model to analyze the attractiveness of the industry. [NOTE: You may NOT an existing web-based Industry Analysis. I will be checking for originality in your analysis]. Michael Porter created a concept known as Porter's Five Forces to help aid in the analysis of an industry's competitive dynamics and attractiveness. The five main factors that influence industry rivalry and determine overall profitability: 1. Threat of New Entrants: this forces assess new competitors that enter the industry. There are factors such as barriers to entry, economies of scale, access to distribution channels, and government regulations that influence the threat level. High entry barriers, such as significant capital requirements or strong brand loyalty, can limit new entrants, making the industry more attractive and potentially more profitable. 2. Bargaining Power of Suppliers: This force evaluates the influence suppliers have on the industry. Suppliers with high bargaining power can demand higher prices or reduce the quality of inputs, impacting the profitability of industry players. Factors such as supplier concentration, availability of substitute inputs, and the uniqueness of suppliers' offerings determine their bargaining power. An industry with numerous alternative suppliers and low switching costs is likely to have weaker supplier power. 3. Bargaining Power of Buyers: This force examines the influence customers have on the industry. Buyers with high bargaining power can demand lower prices, higher quality, or better service, reducing industry profitability. Factors such as buyer concentration, price sensitivity, and switching costs determine buyer power. An industry with fragmented buyers and low switching costs typically has weaker buyer power. 1. Threat of Substitutes: This force considers the availability of alternative products or services that can satisfy customers' needs. Substitutes can limit the pricing power and profitability of an industry. Factors such as the relative price-performance ratio, switching costs, and customer loyalty affect the threat of substitutes. Industries with fewer or less attractive substitute options are generally more favorable. 2. Intensity of Competitive Rivalry: This force analyzes the level of competition among existing industry players. Factors such as the number of competitors, industry growth rate, product differentiation, and exit barriers influence competitive intensity. A highly competitive industry with numerous players, low differentiation, and slow growth may lead to price wars and reduced profitability. Analyzing the attractiveness of the electric vehicle (EV) industry using Porter's Five Forces: 1. Threat of New Entrants: The EV industry has a moderate to high threat of new entrants. While there are barriers to entry such as high capital requirements for manufacturing, established automakers with existing production capabilities can enter the market. Additionally, the increasing availability of electric vehicle technology and the push for sustainability may attract new players, making this force relatively strong. 2. Bargaining Power of Suppliers: The bargaining power of suppliers in the EV industry can vary. Suppliers of key components like batteries may have some leverage due to they're expertise and limited competition. However, as the industry grows and demand for EVs increases, suppliers may face more competition, potentially reducing they're power. 3. Bargaining Power of Buyers: The bargaining power of buyers in the EV industry is relatively high. Buyers have access to various electric vehicle models and can compare prices and features easy. Additionally, government incentives and policies can influence buyer decisions. Overall, buyers have the power to demand competitive pricing, quality, and additional features, affecting industry profitability. 4. Threat of Substitutes: The threat of substitutes in the EV industry is relatively low. Currently, there are limited viable substitutes for electric vehicles, especially in terms of clean and sustainable transportation. While internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles are a substitute, the global shift towards electric mobility and increasing environmental concerns make substitutes less attractive. 5. Intensity of Competitive Rivalry: The competitive rivalry in the EV industry is very high. Established automakers, new entrants, and technological advancements drive an intense competition. Factors such as product differentiation, pricing strategies, and global market share can all make an impact on the level of rivalry. Additionally, the EV industry is characterized by rapid innovation and has a focus on gaining market dominance, which further fuels the competitive intensity! Overall, the electric vehicle industry demonstrates both opportunities and challenges. While the threat of new entrants and the bargaining power of suppliers does pose potential risks. The high bargaining power of buyers and the relatively of a low threat of substitutes can be favorable for the industry profitability. However, the intense competitive rivalry is necessary for companies to constantly create innovation, differentiate their offerings, and effectively manage pricing strategies to maintain a competitive edge.