Porters-Model-of-Competition-Demo
advertisement

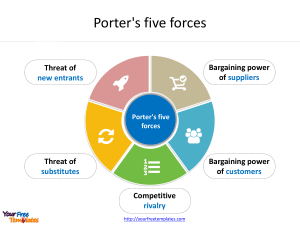
Porter’s Model of Competition Contents Porter’s five forces – Competitor analysis Porter’s generic competitive strategies Porter’s model of competition – Risks and Threats Assessing the balance of power in a business situation Porter’s competitive advantage Porter’s five forces New entrants Suppliers Industry competitors and extent of rivalry & advantage Substitutes Buyers Threat of new entrants The easier it is for new companies to enter the market, greater are the chances of a fierce cut-throat competition. Factors that can limit the threat of new entrants are known as barriers to entry Existing loyalty to major brands Brand equity Incentives for using a particular buyer (such as frequent shopper programs) Switching costs or sunk costs High fixed costs Capital requirements Scarcity of resources Access to distribution Government restrictions or legislation Absolute cost advantages Entry protection (patents, rights, etc.) Learning curve advantages Economies of product differences Expected retaliation by incumbents Competitive rivalry Competitive rivalry amongst companies sometimes extends to non-price dimensions as well like innovation and marketing amongst others Number of competitors Fixed cost allocation per value added Rate of industry growth Level of advertising expense Diversity of competitors Exit Barriers Intermittent industry overcapacity Informational complexity and asymmetry Influencing the power of five forces • Reducing the Bargaining Power of Suppliers • • Reducing the Reducing the Treat of New Competitive Entrants Rivalry between Existing Players • Reducing the Bargaining Power of Customers Reducing the Threat of Substitutes ManagementStudyGuide.com This is a DEMO Course On – Porters Model of Competition. Join MSG Premium Membership and Get Access to around 120 Courses + New courses added every week. What You Get: 1. View All Courses Online. 2. Download Powerpoint Presentation for Each Course. 3. Do the Knowledge Checks for Each Course.







![[5] James William Porter The third member of the Kentucky trio was](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007720435_2-b7ae8b469a9e5e8e28988eb9f13b60e3-300x300.png)
