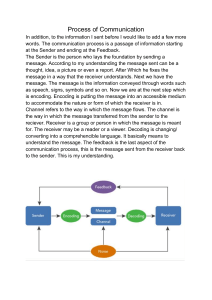
GECC105 PRELIM QUIZ PART 1. Nature and Functions of Communication Identify the function of communication in the following situations: (Regulation, Social Interaction, Motivation, Information) 1. Doctors’ Prescription: “Take your medicine 3 times a day.” 2. Invitation: “Would you like some coffee, tea, or me?” 3. “Did you know that there’s a secret apartment at the top of the Eiffel tower?” 4. Parents’ Instruction to their child: “Wash the dishes now, or else I won’t allow you to go to the party later.” 5. Teacher to student: “You did well in my class today, keep it up!” PART 2. Aristotle’s Model Communication. Supply the following with the correct answer: 1. This model was proposed before ______ B.C 2. Aristotle’s Model is mainly focused on ______ and speech. 3. It is the speaker’s role and responsibility to influence the audience through __________ speaking. 4. He believed __________ is the study of communication and persuasion. 5. It can be broadly divided into five primary elements: Speaker, Speech, Occasion, Audience and ____________. PART 3. Shannon-Weaver Model of Communication. Supply the following with the correct answer: 1. This is often called the _____________ since it was developed because of the technology of the telephone and the experience of “noise” coming from the switchboard. 2. As Shannon was an engineer, this model was first made to improve _____________communication, mainly for telephonic communication. 3. The ______________ encodes the message and sends it to the receiver. 4. The channel can have __________and the receiver might not have the capacity to decode which might cause problems in the communication process. 5. The model was created by American engineer Shannon & Weaver in the year _____________ PART 4. Schramm’s Model of Communication. True or False ______ 1. The Schramm Communication Model offers a classic approach to and explanation of communication. ______ 2. Schramm Communication Model, is a linear communication model containing all the basic principles of communication. ______ 3. The cyclical communication model is based on the theory and belief that communication is a one-way street. ______ 4. The recipient and sender can also be one and the same. ______ 5. The Schramm Communication Model is circular. PART 5. Eugene White’s Stages of Oral Communication Matching Type A. ______ 1. the coding of ideas into the oral language ______ 2. paying attention to signs on how your listener understands your message ______ 3. the receiver’s response to the message ______ 4. the sound waves reaches the receiver’s ears, after which the resulting nerve impulses reaches the brain through the auditory nerves ______ 5. the sound waves carry the sender’s message to the receiver B. A. Thinking B. Symbolizing C. Expressing D. Transmitting E. Receiving F. Decoding G. Feedback H. Monitoring Part 1. 10/10 1. Regulation or Control 2. Social interaction 3. Information 4. Regulation or Control 5. Motivation Part 2. 2 points each 10/10 1. 300 2. Speaker 3. Public 4. Rhetoric 5. effect Part 3 2 points each 10/10 1. “Telephone Model” 2. technical 3. sender 4. noise 5. 1948 Part 4 2 points each 10/10 1. True 2. False 3. False 4. True 5. True Part 5 2 points each 10/10 1. B 2. H 3. G 4. E 5. D