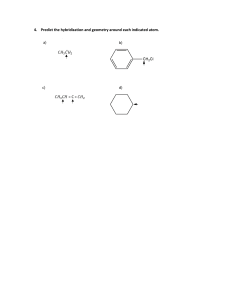
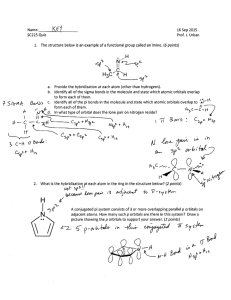
2.7 - VSEPR Molecular Geometry ► 3D arrengement of atoms in a molecule – physical and chemical properties - melting, boiling pointing, density, types of reactions it undergoes. ► Bond lenghts and bond angles – experiment determined ► Simples procedure to predict the geometry – using the number of electrons surrounding a central atom in its Lewis structure. ► Base: electrons pairs in the valence shell of an atom repel one another. VSEPR Model (valence-shell electron-pair repulsion) ► The repulsion between electrons in different bonding pairs causes them to remain as far apart as possible. ► The structure around a given atom is determined principally by minimazing electron pair repulsions. Predicting a VSEPR Structure ► Draw ► Put Lewis Structure pairs as far apart as possible. ► Determine positions of atoms from the way electron pairs are shared. ► Determine the name of molecular structure from positions of the atoms. Predicting a VSEPR Structure Couple of things to keep in mind: ► Lone pairs take up more space than shared pairs ► Multiply bond count as one shared pair ► We divide the molecules into two categories: according to whether or not the central atom has lone pairs. PHET Simulation ► https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/moleculeshapes/latest/molecule-shapes_en.html Remember that lone pairs take up more space than shared pairs Any 2-atom molecule with a polar bond Wich molecules have a dipole moment? With three or more atoms there are two considerations: 1. There must be a polar bond. 2. Geometry cannot cancel it out. Geometry and Dipole Moment ► Examples of Bond that cancel polarity of bonds: Linear Trigonal Planar Obs: Terminal atoms are the same. 120 Geometry and Dipole Moment ► Examples of Bond that not cancel polarity of bonds: Bent Trigonal Pyramidal VSEPR Practice ► Predict the molecular geometry, bond angles and polarity for each of the following molecule or ion: Hybridization ► The mixing of atomic orbitals to form special orbitals for bonding. ► Blending Orbitals ► The atoms are responding as needed to give the minimum energy for the molecule. Weakness of Atomic Orbitals ► … to explains molecular geometry ► In methane, CH4, the shape is tetrahedral. ► The valence electrons of carbon should be two in s, and two in p. ► The atomic orbitals change when making a molecule. Methane Atomic Orbitals 3 sp Hybridization 3 sp Energy Energy How do we kow the hybridization? ► We know the geometry from experiment ► We know the orbitaks of the atom ► Hybridizing atiomic orbitaks explains the geometry ► If the geometry requires a tetrahedral shape, it is sp3 hybridized (bond angle 109.5) ► This includes bent and trigonal pyramiidal. Hybridization depends upon stearic number only!! Stearic number = electron domains = number of electrons pair surrounding the atom 2 sp Hybridization ► Ex. C2H4 ► Double bond acts as one pair ► Trigonal planar geometry ► We need three blended orbitals ► Use one s and two p orbitals to make sp2 orbitals ► Leaves one p orbital perpendicular 2 sp Hybridization 2 sp Energy Energy 3rd p orbital Located perpendicular to the sp2 orbitals 2 types of Bonds ► A sigma (𝞂) bond centers along the internuclear axis (formed from overlapping hybridized orbitals) ► A pi (𝛑 ) bond occupies the space above and below the internuclear axis (formed from unhybridized orbitals) A sigma bond and a pi bond together make a double bond 2 sp Hybridization sp Hybridization ► Ex. CO2 ► Linear geometry ► We need two blended orbitals ► Use one s and one p orbital to make sp orbitals ► Leaves two p orbitals perpendicular sp Energy Energy 2nd and 3rd p orbitals ► Both are located perpendicular to the sp orbital sp Hybridization ► If the geometry requires a linear shape, it is sp hybridized bond angle 180) Hybridization Practice ► Using the diagram below… ► 1. Determine the hybridization around the atomns a-e ► 2. A student claims that all the atoms in the molecule exist in a single plane. Do you agree with the student`s claim? ► Explains why or why not.. Resonance Vocabulary ► 𝞂 bonds can described as being localized ► A resonating 𝛑 bond must be treated as being delocalized ► Ex. No2 _ and NO3 _