Electrochemistry: Electrolytic & Chemical Cells Explained
advertisement

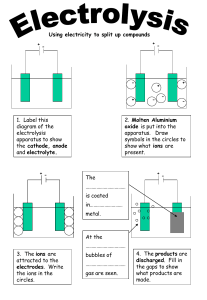
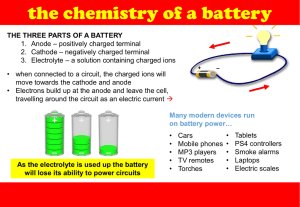
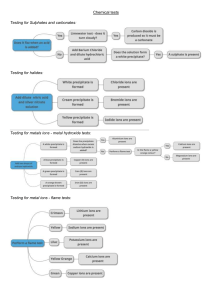
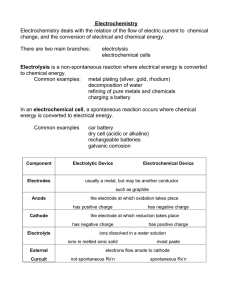
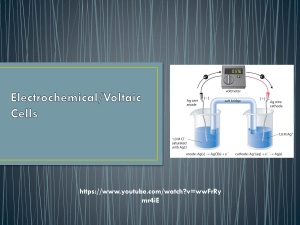
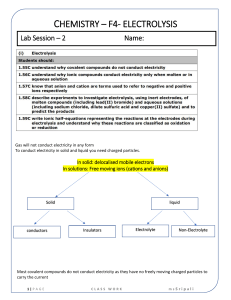
CHAPTER 6 ELECTROCHEMISTRY Electrolyte 6.1 ELECTROLYTIC CELL is a study in chemistry of the relationship between electrical and chemical A. Electrolytic cell Electric current flows through an electrolyte to produce a chemical reaction. Change of energy : Electrical energy Chemical energy Name of process B. Chemical cell Electrolysis Chemical changes that occur in the cell produce an electric current. Chemical energy electrical energy ELECTROLYSIS Decomposition of a compound in the molten or aqueous state into its constituent elements when electric current flows through it. What are the decomposed Source of electric Electrode Battery -To produce electric current to carry out electrolysis Rod that can conduct electricity Anode The electrode connected to the positive terminal. Catho the electrode de connected to the negative terminal. Substances in the m Electrolytes are ionic compounds in the molten or aqueous state which consist of positive ions, (cations) and negative ions, (anions.) *molten-contain 2 ions * aqueous-contains 3 / 4 ions Anions Negative ions (-) Cation Positive ions s (+) During the electrolysis process: Cations move to Cathode Anions move to Anode atoms of the metal which are then deposited at the cathode an electrolytic cell half-filled with 0.1 mol dm–3 copper(II) sulphate solution, CuSO4 , and two test tubes filled completely with 0.1 mol dm–3 copper(II) sulphate solution, CuSO4 FACTORS AFFECTING THE PRODUCTS OF ELECTROLYSIS 1.position Ions at the bottom of the of ions in electrochemical series have the higher tendencies to be electroche discharged. mical series 2. concentrati on of electrolyte 3. types of electrode Negative ions which are more concentrated in an electrolyte are more likely to be discharged at the anode. If the metal used as the anode is the same as the metal ion in the electrolyte, Anode Thinning : the metal atoms will ionise to form positive ions that dissolve into electrolyte Catho Thicker de the metal ions will discharge to form APPLICATION OF ELECTROLYSIS IN INDUSTRIES 1.Extractio To extract metals from their n of metals molten ores or salts (that are more reactive than *factor carbon,)eg: potassium, used: sodium ,calcium, magnesium concentrati & aluminium on of electrolyte Electrode: carbon Electrolyte: ion compound contain metal that be extracted. Eg: Lead bromide Observation: Cathode: Grey metal deposited ( lead) Anode: Brown gas release( bromine gas) Explanation: 6.2 Chemical Cell -A simple chemical cell made up of : 2 different metals immersed in an electrolyte & connected to an external circuit with wires Movement of electrons ANODE to CATHODE Terminal negative to terminal positive Energy change The flow of electrons fr –ve terminal to +ve terminal through the external circuit produce electrical energy Chemical energy to electrical energy Application of Chemical cell concept in Generating electrical energy Natural 1.Fruits/citrus fruits eg Source act orange, lemon as 2.Seawater electrolyte 3.Potato in chemical cell Anode Cathode 1.Metal is more electropositive (easy to loss electron become Mg2+) 2.Magesium act as negative terminal 1.Metal is more electronegative( easy to gain electron become copper atom) 2.Copper act as positive terminal 1.Zn is more electropositive, terminal negative, Cu terminal positive 2.The lemon juice is acidic act as electrolyte allows the eclectrons to get to copper. 3.The flow of electrons produce electrical energy, the bulb is lighted up