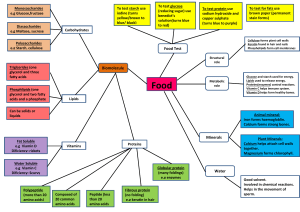
Worksheet for Topic 4 Biological molecules 4.1 Carbohydrates Monosaccharide Disaccharide Polysaccharide Sugar unit One Two Many Example glucose Maltose, sucrose Starch, glycogen, cellulose Polysaccharide Starch Cellulose Glycogen Found in Only in plants Only in plants Only in animals Function Energy storage in plants Make up cell wall Energy storage in animals 4.2 Lipids • Lipids are divided into fats (solids • Most fats (lipids) in the body are made up of triglycerides Triglyceride = 1 glycerol at room temperature) and oils (liquids + 3 fatty at room temperature) acid 4.3 Proteins The basic unit of protein is called amino acid There are about 2 . 0 different amino acids. The structure of amino acid They all contain the same basic structure but the ‘R’ group is different for each one The different sequences of amino acids cause the polypeptide chains to fold in different ways and this gives rise to the different shapes of proteins. Example of protein: enzyme, antibody 4.4 Food test Molecules Starch Reducing sugar Protein Fats Vitamin C Reagent Iodine solution Benedict’s solution Biuret solution Ethanol & water DCPIP Color change Brown→black blue Blue→brick red Blue→ Clean→cloudy Colorless→blue purple/violet (emulsification) Notice Heating required 4.5 DNA structure Nucleus, chromosome, DNA, gene (A): Adenine (C): Cytosine (T): Thymine (G): Guanine Base pairing rules: 4.6 Water Water is important as a solvent Dissolved substances can be easily transported around organisms (digested food molecules, urea, salts) Water is also an important part of the cytoplasm and plays a role in ensuring metabolic reactions can happen as necessary in cells