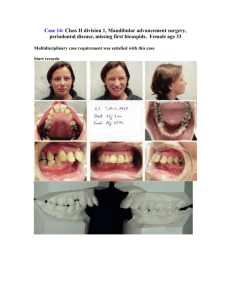
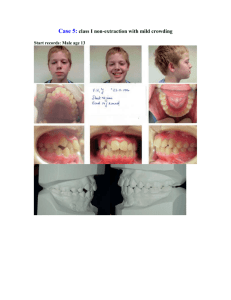
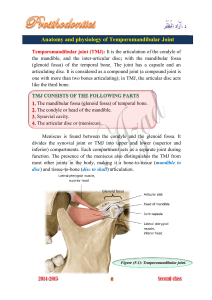
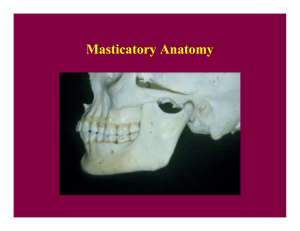
LESSON II ARTICULATIONS TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT Example of ginglymoarthrodial articulation Combination of gliding and loose hinge movement OSSEOUS PORTION OF JOINT 1. MANDIBULAR GLENOID FOSSA 2. ARTICULAR EMINENCE 3. CONDYLOID PROCESS ARTICULAR DISK / MENISKUS Connective tissue found on the temporal bone and mandibular condyle Made up of dense collagenous CN Avascular and no nerve No pain BASIC MANDIBULAR MOVEMENT 1. HINGE Occurs when the condyle undergo ROTATION Occurs when normal mouth opening When there is 2-3 mm intercuspal distance (normal mouth opening) between upper and lower 2. GLIDING Condyle undergo translation Came Out of the glenoid cavity and moved in articular eminence Moves in protrusive lateral movement BENETT SHIFT Lateral movement MANDIBULAR FOSSA Oblong or depression in temporal bone just anterior to auditory canal BOUNDARIES OF MANDIBULAR FOSSA anteriorly : ARTICULAR EMINENCE externally : MIDDLE ROOT OF ZYGOMA AND AUDITORY TUBE Posteriorly : TYMPANIC PLATES MANDIBULAR CONDYLE / CONDYLOID PROCESS Convex on all bearing surfaces although somewhat flattened posteriorly Wider latero posteriorly and thinner antero posteriorly is thinner than latero medially BASIC PARTS OF MANDIBULAR CONDYLE 1. LATERAL POLE 2. MEDIAL POLE 3. PTERYGOID FOVEA Attachment of LATERAL PTERYGOID MUSCLE o Depression of mouth JOINT CAPSULE Where TMJ is enclosed Attached at the articulation process of mandibular fossa, eminence of the temporal bone and to the neck of the mandible CONSIST OF: 1. INNER SYNOVIAL LAYER 2. OUTER FIBROUS LAYER Contains nerves veins and collagen fibers Nerve innervation:TRIGEMINAL NERVE Vascular supply : MAXILLARY, TEMPORAL AND MASSETERIC ARTERIES ANTEROLATERAL SIDE Thickened forming a band called temporomandibular ligament TEMPOROMANDIBULAR LIGAMENT Originate on the zygomatic arch Passes backwards attached on the lateral surface and neck of the mandible 3 MANDIBULAR LIGAMENT 1. STYLOMANDIBULAR LIGAMENT Origin : STYLOID PROCESS insertion: ANGLE OF MANDIBLE Action: Limit excessive anterior drift 2. SPHENOMANDIBULAR LIGAMENT Origin :ANGULAR SPINE OF THE SPHENOID BONE insertion: LINGULA OF MANDIBLE Action: Main suspensory drift for wider mouth opening. 3. TEMPOROMANDIBULAR LIGAMENT Origin : OUTER SURFACE OF THE ARTICULAR EMINENCE AND THE POSTERIOR SURFACE OF ZYGOMATIC ARCH insertion: BEHIND AND BELOW THE CONDYLAR NECK Action: Limit excessive posterior drift Main suspensory drift for normal mouth opening. NOTE: Part of masticatory apparatus and has no direct effect in mandibular elevation and depression Help stabilize the jaws and has no direct relationship with ma mandibular articulation BASIC TYPE OF ARTICULATION 1. SYNARTHROSIS Suture Gomphosis synchondrosis 2. ARTICULAR DISK Has thicker anterior and posterior bands Has thin central zone that are evident ATTACHMENT OF ARTICULAR DISK Anteriorly Attachment: LATERAL PTERYGOID MUSCLE Posterior attachment : RETRODISCAL TISSUE BASIC POSITION OF MANDIBLE 1. CENTRIC RELATION Relaxed position Normal mouth opening Has 2-3mm space between maxilla and mandibular teeth Hinging 2. CENTRIC OCCLUSION Maximum intercuspation Where in the condyle is in most protruded position HIging CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE FOR CENTRIC OCCLUSION condyle is in most protruded position Fabrication of normal occlusion 1. 3. LOOKING UP Muscles of the neck pull mandible towards posterior 2. SWALLOW To achieve normal bite STRESS THE MUSCLE OF MASTICATION Cause of TMD 1. When loose the vertical dimension of occlusion 2. SPASM occurs on muscle of mastication NOTE: Present of pain in TMD because of the retrodiscal tissue impinge between condyle and temporal bone which is vascular and contains nerve ending rather than meniscus which is 3. AMPHIARTHROSIS Syndesmosis DIARTHROSIS - freely movable TMJ ATLANTO- OCCIPITAL JOINT nodding movements Synovial articulation to superior articular facet of atlas and occipital condyles of skull ATLANTOAXIAL JOINT Joint in saying no C1-C2 Do not have an intervertebral disc nor an intervertebral Synovial articulation of inferior articular facet of atlas and superior articulating facet of axis