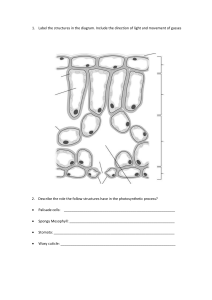
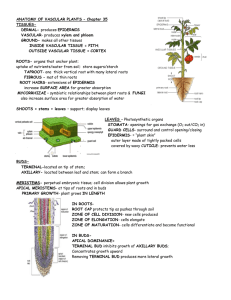
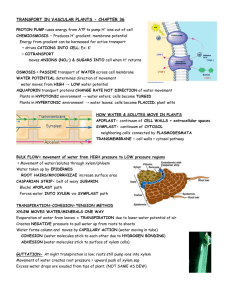
Root hair cell Function: Root hair cells absorb water from the soil by osmosis. Structure: Large surface area Large vacuole for a low water potential level so water can be absorbed by osmosis. Thin cell walls. Xylem Function: Transports water and minerals from the roots up the plant stem and into the leaves. Structure: Most of the cells that make up the Xylem are specialised and called vessels. The vessels lose their end walls so the xylem forms a continuous, hollow tube. Strengthened by a chemical called lignin (research lignin using the textbooks) Phloem Function: Moves food substances that the plant has produces by photosynthesis to where they are needed. Structure: The phloem consists of living cells: sieve tubes and companion cells. Sieve tubes – specialised for transport and have no nuclei, each sieve tube has a perforated end and are connected together. Companion cells – transport of substances in the phloem requires energy. Companion cell provides this energy.