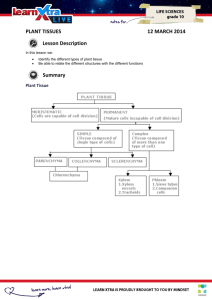
GRADE 10 CELLS AND TISSUES TEST 50 Marks Sclerenchyma tissue may form in small groups or be scattered throughout other cells. Sclerenchyma has thick, secondary, often ______R_____ cells with no ______S_____. Two distinct forms can be noted, these are _____T______ or fibres. QUESTION 1: Read the following passage, then, fill in the missing words, from the list below and Xylem is a structurally and functionally complex tissue, which in conjunction with the write only the missing word and its letter on your answer page. _____U_______ is continuous throughout the plant. It consists of several kinds of cells, and is primarily concerned with water ______V_____. The vessels are _____A____ cells form a continuous layer on the surface of the plant body. They _____W_____ shaped and are joined end to end with each other. Phloem tissue may show various structural modifications in relation to their position. Other epidermal be primary or secondary in origin. It is concerned with the _____X_____ of food stuffs cells are ____B____ of the stomata and ___C____ hairs. The epidermis may also and with support. The principal conducting cells are called sieve cells and sieve tubes. contain ____D___ cells and sclenerchymatic cells. The most distinctive _____E_____ Sieve tubes are joined end to end with each other and are associated with of epidermal tissue is that it is coated with a waxy cuticle. This provides a ______Y______. Supporting cells are the fibres and rays. _____F____ function, and also prevents the leaf from _____G_____. Word List ____H___ tissue is composed of living cells that are capable of growth and even division. It is involved in wound healing, ____I____ and formation of adventitious roots. _____J_____ is a derivative of ____K___, and is found in highest concentrations in the leaf ____L____. _____M_____ is a living tissue that is related to parenchyma. These cells can occur in strands, or in continuous cylinders near the surface of the plant ___N____ and _____O____. The most distinctive feature of this tissue is the cellulose thickened ______P_____ of the cells. These are ideal for supporting and strengthening the _____Q_____ parts of plants, where collenchyma is located. sclereids chisel Epidermal desiccation stems aerial Transportation guard cells feature Derivative phloem translocation guard cells Parenchyma leaves lignified sieve tubes root protective regeneration conduction companion cells cells. Collenchyma corners protoplasm sclerenchyma gland Chlorenchyma mesophyll (25) Question 2 2.1 What is the living material of the cell known as? 2.2 What is the primary difference between inorganic and organic compounds? 2.3 (2) What is the name of the nucleic acids found in the chromatin network? 2.4 (1) (2) In a given cell the following organelles/structures were observed: cell membrane, ribosomes, leucoplast, centriole, cell wall, nucleus, mitochondria, chromoplasts, large vacuole. 2.4.1 Give four reasons as to why the cell is a plant cell. 2.4.2 State the functions of (i) the vacuole, (ii) ribosomes, and (iii) mitochondria. (4) (3x2) /15/ Question 3 3.1 Sketch and label a diagram of a generalised animal cell. Provide at least 10 different labels, including the title Total marks 50 (10)