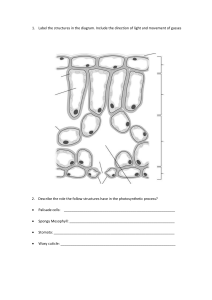
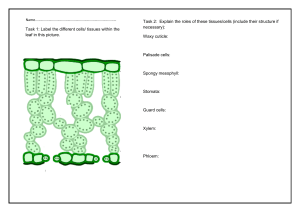
Grade 11 Term 1 Test MEMO QUESTION 1 (10) Choose the best option and underline the most correct answer (letter) on your folio paper: (1 mark each) 1.1 a The main function of phloem in a stem is to: transport water only b c give mechanical support d 1.2 a c Root hairs: cause elongation of the root anchor a plant into the soil b d 1.3 a c The wood of the bench on which you sit consists mainly of: phloem tissue b bark vascular cambium d xylem 1.4 a c The bark of a tree is produced by: primary phloem vascular cambium b d mature bark cells cork cambium 1.5 a c A plant cell does not need to use energy in: diffusion metabolism b d active transport growth and development transport water and mineral salts translocate sugar are unicellular differentiate to produce root tissue 1.6 The process that plays the most important role in the upwards movement of water in a plant stem is: a plasmolysis b osmosis c transpiration d guttation 1.7 a c Which of the following will increase the transpiration rate? sunken stomata b large leaf area thickened cuticle d rosette arrangement of leaves 1.8 a c The evaporation of water in vapour from leaves is known as: transpiration b respiration guttation d translocation 1.9 a c The tissue that performs the function both of conduction and mechanical support is: sclerenchyma b xylem collenchymas d epidermal tissue Question 10: Which of the following is not associated with phloem? a parenchyma b vessels c sieve tubes d fibres QUESTION 2 (10) 1 Answer tapered F A An elongated thick walled conductive cell of xylem 2 Modified epidermal cells, which control gaseous exchange in leaves 3 Dividing tissue responsible for the production of bark 4 The name given for the transport of dissolved organic food within a plant 5 The perforated horizontal end walls in sieve tubes 6 The living nucleated cells that form part of phloem tissue 7 The completely permeable part of a plant cell 8 The state of a cell that is firm and stiff due to water uptake 9 The loss of water in vapour form from arial parts of a plant 10 The movement of water molecules through a differentially permeable membrane Companion cells D B Cork cambium B C Translocation C D Guard cells E E Sieve plates A F Tracheids J G Osmosis I H Transpiration H I turgid G J Cellwall QUESTION 3 (14) Study the diagram below and answer the questions 3.1 Label the above diagram (7) Number Label 1 Root hair 2 Epidermis 3 Parenchyma 4 Endodermis 5 Cortex 6 Phloem 7 Xylem 3.2 Where is food stored in a root? (1) Cortex Parenchyma 3.3 The root epidermis is not coated with waxy cuticle. Why not? (3) A waxy cuticle being waterproof would prevent water being absorbed, which is a major function of roots. 3.4 What does the stele of a root consist of? (3) The stele consists of vascular tissue, xylem and phloem QUESTION 4 (6) Study the diagram below and answer the questions 4.1 What is the approximate age of this tree? (2) 4 years 4.2 Which labelled part represents the spring growth? (2) No 2 4.3 In which numbered part are cork cells found? (2) No 1 QUESTION 5 (15) The diagrams shown here represent the leaves of the seedlings of a mesophyte, transplanted at different times during a warm summer month. One seedling was transplanted at 12h00 and the other at 20h00. All other factors were the same for both seedlings during transplantation. 5.1 Study the diagrams and answer the following questions. 5.1.1 Which diagram shows the seedling transplanted at 12h00? Diagram 2 (1) 5.1.2 Give an observable reason for your answer to 5.1.1 Leave cells/leaves are wilted (1) 5.1.3 Explain the reason given in question 5.1.2 (2) Seedlings was transplanted in the afternoon Transpiration takes place due to high temp Water is lost but not replaced during transplant Roots have not started to absorb water because seedling was transplanted very recently 5.2 Study the diagrams below and answer the questions that follow. 5.2.1 Name the processes that have taken place in cell 1 and twig G respectively (1) Plasmolysis wilting 5.2.2 Identify parts A, B, C, D and E A: Cell membrane B: Cell wall C: Nucleus D: Cytoplasm E: Vacuole (5) 5.2.3 Which cell could have been placed in hypertonic solution? Cell 1 (1) 5.2.4 Which cell can be associated with twig: a) F b) G F – Cell 2 G – Cell1 (2) 5.2.5 Explain your answer to question 2.4. (2) Water lost through transpiration is being replaced by absorbed water, and therefore the cells remain turgid. QUESTION 6 (5) 6.1 Phloem 6.2 Companion cell 6.3 Source cell 6.4 Sink cell 6.5 Translocation (5)