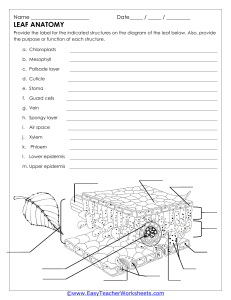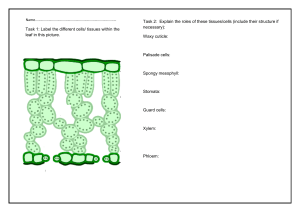
The different types of plant cells found in six organs of the plant body MERISTEMATIC TISSUE A.K.A MERISTEMS :Characterized by small cells, thin cell walls, large cell nuclei, absent or small vacuoles and no intercellular spaces. :Apical (located at root and shoot tips), lateral (in the vascular and cork cambia), and intercalary (at internodes, or stem regions between the places at which leaves attach, and leaf bases, especially of certain monocotyledons) :Primary meristematic tissue helps the plant increase in length or vertical growth, meaning it helps the plant grow up toward the sun and down into the soil. Secondary meristematic tissue helps the plant increase the girth or lateral growth of its stems, branches, and roots. 2 PARENCHYMA :Composed of thin-walled cells and makes up the photosynthetic tissue in leaves, the pulp of fruits, and the endosperm of many seeds. :Found in many parts of the plant body.This is most commonly found in the medullary rays, the pithand the cortex of the wood. It is also found as a packing tissue phloem and xylem. It is mostly found in the softer parts of the plants. :They function in storage, photosynthesis, and as the bulk of ground and vascular tissues 3 COLLENCHYMA :composed by elongated living cells of uneven primary thick walls, which possess hemicellulose, cellulose, and pectic materials. :found immediately under the epidermis, young stems, petioles, and leaf veins. Also, it has been seen in avocado fruit hypodermis. :Provides support, structure, mechanical strength, and flexibility to the petiole, leaf veins, and stem of young plants, allowing for easy bending without breakage. SCLERENCHYMA :have thick, lignified secondary walls, lack cell contents at maturity, and occur throughout all plant tissues. These features make sclerenchyma tissues hard, rigid, and somewhat brittle. :They are found mainly in the cortex of stems and in leaves. :Sclerenchyma tissue, when mature, is composed of dead cells that have heavily thickened walls containing lignin and a high cellulose content (60%– 80%), and serves the function of providing structural support in plants. 5 GUARD CELLS :Guard cells are cells surrounding each stoma. Each guard cell has a relatively thick cuticle on the pore-side and a thin one opposite it. :Guard cells are surrounded by stomatal pores and are located in leaf epidermis. :Guard cells control influx and efflux of CO2 and water from leaves, respectively. 6 TRICHOME CELLS :Trichomes are either glandular or non-glandular. :Different types of non-glandular trichomes can be found in different locations of a single plant. For instance, whole some of these can be found on the leaf of the plant (unicellular non-glandular trichomes on Coridothymus capitatus) two-celled trichomes can be located at the base of abaxial side of the leaf. :Can be insulating by keeping frost away from leaf cells. They can help reduce evaporation by protecting the plant from wind and heat. In many cases, trichomes protect plants from herbivorous insects that may want to feed on them. 7 EPIDERMAL CELLS :Leaf epidermal cells are usually irregular or polygonal in shape. :In plant’s leaves, epidermal cells are located on the upper and lower part of the leaf where they form the upper and lower epidermis. The cuticle, however, is located on the upper epidermis for the most part. In plants, this is the outermost part that is secreted by the epidermis. 8 :Forms a boundary between the plant and the external environment, serves several functions: it protects against water loss, regulate gas exchange, secretes metabolic compounds, and (especially in roots) absorbs water and mineral nutrients. FIBER CELLS :They are long, cylindrical, tubular cells with tapering conical ends, unbranching, and not perfectly round in cross section. The number of fibers varies from 50 to 300 in each fasciculus (bundle). :They often occur in bundles or strands and can be found almost anywhere in the plant body, including the stem, the roots, and the vascular bundles in leaves. :function as support tissue in plant stems and roots. 9 PHLOEM CELLS A.K.A transfer cells and border parenchyma cells :Phloem consists of living cells arranged end to end. Phloem vessels contain cytoplasm, and this goes through the holes in the sieve plates from one cell to the next. :Located near the finest branches and terminations of sieve tubes in leaf veinlets, where they also function in the transport of foods. :Phloem transports sucrose and amino acids up and down the plant. This is called translocation. 10 XYLEM CELLS :The xylem tracheary elements consist of cells known as tracheids and vessel members, both of which are typically narrow, hollow, and elongated. :Can be found: in vascular bundles, present in nonwoody plants and non-woody parts of woody plants. in secondary xylem, laid down by a meristem called the vascular cambium in woody plants. :Xylem, plant vascular tissue that conveys water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant and also provides physical support. 11 PHLOEM AND XYLEM CELLS 12 SIEVE TUBES :Consist of sieve elements which are elongated cells, connected to each other via sieve plates to form a continuous tube system that spreads out through the entire plant. Mature sieve elements contain structural phloem specific proteins (Pproteins), mitochondria, ER, and sieve elements plastids. :It is found in the phloem of all the angiosperms and flowering vascular plants. It is located inside sieve cell. :Sieve tube members maintain cells and transporting necessary molecules with the help of companion cells. The sieve tube members are living cells (which do not contain a nucleus) that are responsible for transporting carbohydrates throughout the plant. 13 COMPANION CELLS :Have dense protoplasts which contain the typical organelles of plant cells, including chloroplasts and many ribosomes. :found within the phloem of flowering plants. :Its function is uncertain, though it appears to regulate the activity of the adjacent sieve element and to take part in loading and unloading sugar into the sieve element. 14 THANK YOU! -DANIELLE SKYLAR DALMAN PAWAI 15 Extra resources 16 17