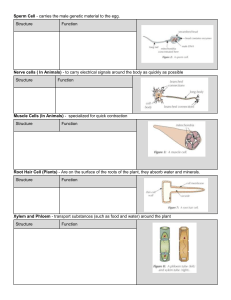
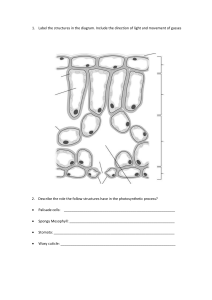
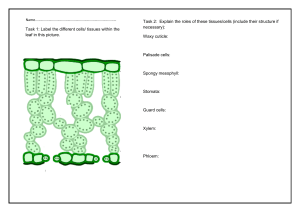
Transport in Plants Contents Transport System of Flowering plants What is Xylem? What is Phloem? Structure of Xylem Structure of Phloem Ion Uptake Transport system of flowering plants • The vessels that transport materials in plants is known as the vascular tissue. • There are two main transport tissues: Xylem Phloem What is Xylem? • Xylem is a plant vascular tissue that conveys water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant and also provides physical support. • Together with phloem , xylem is found in all vascular plants, including the seedless plants: ferns, horsetails, as well as all flowering plants . What is Phloem? Phloem is the vascular tissue in charge of transport and distribution of the organic nutrients ,in particular the sugar sucrose. The phloem is also a pathway to signaling molecules and has a structural function in the plant body. Vascular Tissue • The primary components of vascular tissue are the xylem and phloem. These two tissues transport fluid and nutrients internally. • The two are separated by the CAMBIUM. • The cambium divides and differentiates to form new xylem and phloem tissues. Structure of Xylem • Xylem tissue consists mainly of Xylem Vessels. • A xylem vessel is a long hollow tube made of many dead cells. • Inner walls are strengthened by lignin rings or spirals. Stages of cell division Structure of Consists of two elements: Phloem sieve tube and companion cells. Sieve tube cells or sieve tube elements Elongated, thin walled LIVING cells Cells separated by sieve plates Cross walls that are perforated with pores = sieve Sucrose is loaded into the sieve tube by active transport. Phloem consists of: Sieve Tube cells • • • • • Mature sieve-tubes has thin lining of cytoplasm. Nucleus, central vacuole as well as most organelles are disintegrated. Degenerated protoplasm Sieve tube cells need help to sustain life Companion cells ‘accompany’ them and ‘feed’ them. Companion Cells • • • • • • Each sieve tube cell has a companion cell beside it This carries out the metabolic processes to keep both cells alive Structure: narrow,thin-walled,many mitochondria. Has cytoplasm and a nucleus Function: Provides nutrients and helps sieve tube cells transport food. Stages of cell division Ion Uptake • Plants absorb water from the soil by osmosis. They absorb mineral ions by active transport, against the concentration gradient. Root hair cells are adapted for taking up water and mineral ions by having a large surface area to increase the rate of absorption. • They also contain lots of mitochondria, which release energy from glucose during respiration in order to provide the energy needed for active transport. Purposes of Absorbed Nutrients The absorbed water is transported through the roots to the rest of the plant where it is used for different : purposes It is a reactant used in photosynthesis. 01 02 03 It supports leaves and shoots by keeping the cells rigid. It cools the leaves by evaporation. 04 It transports dissolved minerals around the plant. Stages of cell division