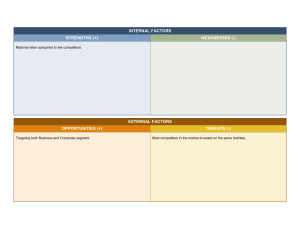
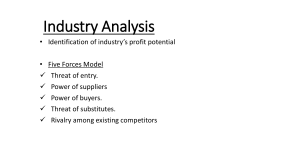
Competition in the industry (High) With more than 25 well established competitors and unknown number of unorganized and local players, the market is monopolistic in nature, with cut throat competition in almost all segments. Potential of new entrants into the industry (Medium) Barrier to entry for a new entrant is low if the target segment is small and locally distributed. Thus, a new player with a limited portfolio, targeting a niche segment or limited geographical area will pose a threat to the established players in that segment and region. Since FMCG industry relies heavily on distribution, making a pan India presence will entail high entry barrier. Power of suppliers (High) power of suppliers is high, since the major raw materials required are alike to a great extent. With several competitors vying for same supplies, the suppliers have a higher bargaining power. Power of customers (High) With more than 25 competitors providing similar offerings in the similar price range, the purchasing power of the customers is high. Companies cannot expect brand loyalty, especially for daily consumable goods that have low investment in terms of money and customer involvement. Threat of substitute products (Medium) Though most of the consumers are already habituated to the consumable products that FMCG companies provide, India is a market where ayurveda and other household remedies are still prevalent and in use. These alternatives may provide some amount of threat through form competition.