Tissues data table
advertisement

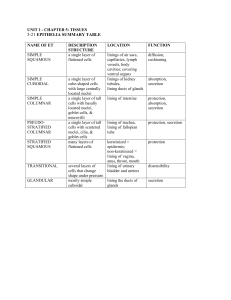
EPITHELIA SUMMARY TABLE NAME OF ET SIMPLE SQUAMOUS SIMPLE CUBOIDAL SIMPLE COLUMNAR PSEUDOSTRATIFIED COLUMNAR STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS TRANSITIONAL GLANDULAR DESCRIPTION STRUCTURE a single layer of flattened cells a single layer of cube-shaped cells with large centrally located nuclei a single layer of tall cells with basally located nuclei, goblet cells, & microvilli a single layer of tall cells with scattered nuclei, cilia, & goblet cells many layers of flattened cells several layers of cells that change shape under pressure mostly simple cuboidal LOCATION FUNCTION linings of air sacs, capillaries, lymph vessels, body cavities; covering ventral organs linings of kidney tubules, lining ducts of glands diffusion, cushioning lining of intestine protection, absorption, secretion lining of trachea, lining of fallopian tube protection, secretion keratinized = epidermis; non-keratinized = lining of vagina, anus, throat, mouth lining of urinary bladder and ureters protection lining the ducts of glands secretion absorption, secretion distensibility CONNECTIVE TISSUE SUMMARY TABLE NAME OF CT AREOLAR ADIPOSE DESCRIPTION gel-like matrix with fibroblasts, collagen and elastic fibers closely packed adipocytes with nuclei pushed to one side LOCATION beneath ET (serous membranes & mucous membranes) beneath skin (as subcutaneous layer), breasts, around kidneys & eyeballs basement membranes, lymphatic organs tendons, ligaments DENSE REGULAR DENSE IRREGULAR ELASTIC network of ret. fibers in loose matrix dense matrix of collagen fibers loose matrix of collagen fibers matrix of elastic fibers HYALINE CARTILAGE chondrocytes in lacunae in amorphous matrix FIBROCARTILAGE ELASTIC CARTILAGE BONE less firm than above with collagen in matrix above plus elastic fibers concentric circles of calcified matrix skeleton BLOOD red cells, white cells and platelets in liquid plasma in heart and blood vessels RETICULAR dermis of skin walls of large airways, wall of aorta embryonic. skeleton, costal cart, tip of nose, trachea, larynx intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis external ear, epiglottis FUNCTION diffusion, cushioning organs, lubrication insulation, energy store, protection Support attachment (high tensile strength) tensile strength durability with stretch Support tensile strength, shock absorber shape maintenance plus flexibility support, protection, movement, Ca ++ store, hematopoiesis transport of nutrients, wastes & gases MUSCLE TISSUE SUMMARY TABLE NAME OF MUSCLE TISSUE SKELETAL MUSCLE SMOOTH MUSCLE CARDIAC MUSCLE DESCRIPTION OF STRUCTURE long, thin fibers with many nuclei and striations spindle shaped cells with one centrally located nucleus, lacking striations TYPE OF CONTROL LOCATION FUNCTION Voluntary attached to bones to move bones Involuntary Visceral Smooth Muscle: walls of visceral hollow organs Multiunit Smooth Muscle: irises of eyes, walls of blood vessels a network of striated cells with one centrally located nucleus attached by intercalated discs Involuntary heart to move substances through passageways (i.e. food, urine, semen), constriction blood vessels, etc. pump blood to lungs and body