Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 5 Practice Test (Test worth 44 pts
advertisement

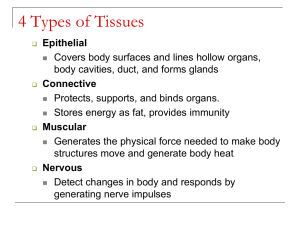
Histology is the study of what? Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 5 Practice Test (Test worth 44 pts) What are the epithelial tissues major functions? Epithelial tissues are characterized by a lack of blood vessels. A. True B. False What is the name of the tissue through which gases are exchanged between the blood and the air in the lungs? What is a base membrane, and where does it occur? What type of tissue forms the inner lining of the respiratory passages? The type of muscle tissue that can be consciously controlled is known as what? The type of epithelium that lines the urinary bladder and many of the urinary passageways is known as what? Smooth muscle is located where? Describe loose connective tissue. The type of cells that reside in a specific connective tissue type for an extended period of time are called what? What are the four basic types of body tissues? Tendons and ligaments are composed primarily of what type of tissue? Connective tissue fibers are produced by what type of cell? The type of muscle tissue found in blood vessels is known as what? Injured fibrous connective tissue and cartilage are slow to heal because … Cardiac muscle is found where? Write the name of the type of tissue next to its description. Most abundant tissue by weight, bind structures, provide protection, fill spaces, stores fat, good blood supplies Rigid, provides support, lacks a direct blood supply so healing is very slow Layers of cube-shaped cells- lines the mammary glands, sweat glands, and provides protection Involuntary, comprises the walls of hollow internal organs ex: digestive tract Single layer of thin flattened cells, lines the air sacs of the lungs Many layers of cells, tissues are thick, cells near the surface are flattened the most, outer layer of the skin Appear layered, but are not, have cilia, lines the passage way of the respiratory system Top cells are elongated, lower cells are cuboidal, found in the urethra Fibers in branching networks, attachments between the bones of the spinal column Attached to bones, controlled by conscious effort Forms thin membranes, binds skin to underlying tissue Strong, can withstand pulling forces, binds body parts together, make-up tendons and ligaments Only in the heart Found in the brain and spinal cord, can sense changes in its surroundings and respond Found throughout the body, covers body surfaces, always has a free surface, anchored to a basement membrane, lacks blood vessels Most rigid, supports body structures, attached to muscle Consists of RBC, WBC¸ Platelets, and plasma, transports gases, and fights infections Fat, lies beneath skin, cushions joints, insulates- stores energy ***Be able to identify the 3 types of muscle tissue and nervous tissue by looks. Single layer of cube shaped cells, lines the thyroid gland and covers the ovaries Thin fibers, makes up the framework of certain internal organs such as the liver and spleen Specialized to change in response to increased tension- lines the bladder Single layer of elongated cells, with the nuclei near the basement membrane, can be cilated or nonciliated, secretes digestive fluids, and absorbs nutrients from digested foods