LV. CNM 2012-12-18 14457
advertisement

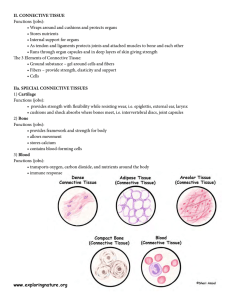
Tissues – Types of tissues Epithelial o Cover organs and lines body surfaces o Made of tightly packed cells (lacks blood vessels, replaced frequently, prominent nuclei) o Simple—single layered, used for diffusion and filtration o Stratified—two or more layers, best suited for protective materials because it can loose layers of cells Keratin hardens and makes a protective shell, blocks chemicals and microorganisms, keep liquids in o Function in secretion, absorption, excretion o Types: Squamous—tightly packed flattened cells Cuboidal—cubed shaped Columnar—elongated Pseudostratified ciliated columnar—appears to be stratified, but its not (this is due to the nuclei), and has cilia Transitional—changes in response to pressure Glandular—made up of cells designed to secret substances into body fluids Connective o Binds, supports, protects, serves as frameworks, fill spaces, store fats, produce blood cells, fight infection, repair tissue damage o Have a matrixnonliving material surrounding the cells o Fibers found are: collagenous, reticular fibers, and elastic fibers o Cells types: Fibroblasts: produce fibers Macrophages: produced from white blood cells Most cells: release heparin (prevents blood clotting) Historine: promotes reaction o Types: Loose fibrous connective—binds the skin to underlying organs and fills space between muscles Dense connective tissue—found all over body, found in tendons, ligaments, deep skin layer Cartilage—is a rigid connective tissue that provides a supportive framework for various structures o Most common type is the hyaline (found in ends of bones, part of nose, respiratory passages) o Elastic cartilage—very flexible (found in ear) o o o Fibrocartilage—is the toughest of the three (found in vertebrae of spinal chord, in knees) Bone—cells and matrix for concentrically shaped circles around a central canal Blood—maintain stable internal environmental conditions, transportation, exchanges of substances, composed of formed elements and a liquid blood plasma Muscle o Function is to contractmoving body parts o Skeletal muscle tissue Found attached to bones Cells appear striped and are striations Voluntary muscle contractions Long parallel fibers o Smooth muscle Found in the walls of internal organs Shape of cells—spindle shaped One single central nuclei Involuntary o Cardiac muscle Cells also appear striped or striated Branching cells Distinct plate-like structure between connecting cells Found in the heart and is branched It is involuntary Nerve o o o o Nerve cells sense certain types of changes Carry impulse Neurons – primarily elongated cells with long extensions or branches. Support cells that care for the neurons.