MLAB 2401: Clinical Chemistry Keri Brophy-Martinez Parathyroid gland

MLAB 2401: Clinical Chemistry
Keri Brophy-Martinez
Parathyroid gland
Anatomy
• The parathyroid glands are four or more small glands located on the posterior surface (back side) of the thyroid gland.
Function & Regulation
• Maintain the body’s calcium level for proper functioning of nervous and muscular systems
High blood Ca + level
Breakdown of bone matrix decreases
• In situations of low blood calcium, the parathyroid senses this and releases PTH hormone that work to increase calcium levels
Normal blood Ca + Level
Low blood
Ca + level
Breakdown of bone matrix increases
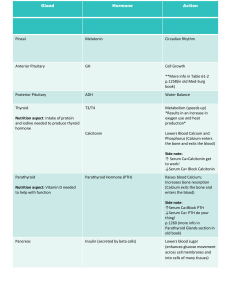
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
• Sole hormone secreted by parathyroid, from the chief cells
• Also known as parathyrin
PTH
• Action
– Raise serum concentration of calcium
– How?
• Promotes reabsorption of calcium from bone
• Increases kidney tubule reabsorption of calcium by a process where phosphate and bicarbonate is excreted
• Activates vitamin D, assists in absorption in the gut
Calcitonin
• Produced by the thyroid
• Action
– Increase bone formation
– Inhibit bone breakdown
– Lowers blood calcium levels
– Antagonistic to PTH
Disorders
• Hyperparathyroidism
– Causes
• Benign adenoma
• Hyperplasia of tissue in response to chronic calcium loss
• Secretion of PTH from malignant non-endocrine tumor
Hyperparathyroidism
• Results
– Increased PTH
– Increased urine and serum calcium
– Decreased serum phosphorous
– Increased urine phosphorous
– Kidney problems (stones)
– Bone problems (demineralization)
Hypoparathyroidism
• Causes
– Primary
• Idiopathic
– Secondary
• Thyroid/ parathyroid surgery
• Autoimmune diseases
• Results
– Decrease PTH
– Decreased serum calcium
– Increased serum phosphorous
References
• Bishop, M., Fody, E., & Schoeff, l. (2010). Clinical Chemistry:
Techniques, principles, Correlations. Baltimore: Wolters Kluwer
Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
• http://www.cedars-sinai.edu/Patients/Programs-and-
Services/Head-and-Neck-Cancer-
Center/Treatment/Parathyroidectomy.aspx
• http://www.teachpe.com/gcse_anatomy/bones.php
• Sunheimer, R., & Graves, L. (2010). Clinical Laboratory Chemistry.
Upper Saddle River: Pearson .
10