Endocrine Fellows Test
advertisement

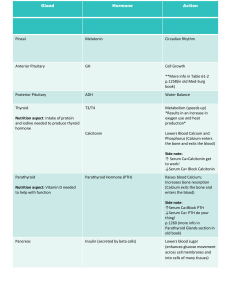
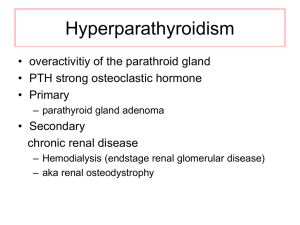
Endocrine Fellows Test Calcium Metabolism/Pituitary __________1. The half life of intact PTH is a.30 minutes b. 60 minutes c. 2 minutes d. 120 minutes __________2. The primary site for hormonal regulation of renal calcium reabsorption is a. thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop b. proximal renal tubules c. Distal renal tubules d. Descending limb of Henle’s loop __________3. Syndrome composed of pituitary tumor, parathyroid tumor and pancreatic islet tumor a. MEN 2a b. MEN 2b c. RET gene mutation d. Inactivating mutations on the tumor suppressor gene encoding menin __________4. A 45 year old complains of body weakness, bone pains , epigastic pain and nausea the past 6 months. Serum calcium is 12.5 mg/dl. Urinary calcium is 500 mg/day. KUB showed nephrolithiasis. Intact PTH was elevated . Tc 99m Sestamibi scan showed solitary parathyroid adenoma. Treatment is a. removal of 3 1/2 parathyroid glands b. removal of 4 parathyroid glands with autotransplantation of parathyroid fragments in forearm c. medical follow up d. unilateral parathyroidectomy . __________5. Successful removal of parathyroid tumor is indicated by a. PTH return to normal within 30 hours b. Normal serum calcium within 24 hours c. Intraoperative drop in PTH of greater than 30% d. Normal PTH within 6 months. _________6. Parathyroid independent hypercalcemia a. familial hypocalciuric hypercalciuria b. primary hyperparathyroidism c. adrenal insufficiency d. chronic renal failure __________7. Effective antiresorptive therapy on nonvertebral fracture a. raloxifene b. calcitonin c. ibandronate d. zoledronate __________8. A 42 year old patient returns two weeks post transphenoidal surgery for growth hormone secreting pituitary tumor. Which test is best to determine cure? a. insulin tolerance test b. serum insulin -like growth factor binding protein 3 c. serum insulin -like growth factor d. glucose suppression test for growth hormone __________9. The best screening test for growth hormone pituitary tumor is a. insulin tolerance test b. serum insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 c. serum insulin-like growth factor d. glucose suppression test for growth hormone. ___________10. 50 year old female presents with severe headache blurring of vision and nausea unrelieved by acetaminophen. Medical history is hypertension with intake of aspirin and irbesartan. Physical examination is BP 110/80 HR 92/minute. Neorological exam CN III deficit . Lab exams Na 135 K 4.0 creatinine 1.5 platelet count normal RBS 80 mg.dl. CT scan showed sellar mass with acute hemorrhage. The first step to do is: a. surgical decompression b. ventriculostomy c. glucocorticoid therapy d. gamma knife radiosurgery ________11. The gold standard for assessing ACTH reserve is a. plasma ACTH b. insulin tolerance test c. 24 hour urinary free cortisol d. Cosyntropin stimulation test ________12. Treatment for prolactin producing macroadenoma a. Bromocriptine b. Surgery c. Gamma knife surgery d. Octreotide ________13. Growth hormone receptor antagonist a. cabergoline b. lanreotide c. pegvisomant d. octreotide ________14. Wolfram Syndrome consists of a. diabetes insipidus, diabetes mellitus, optic atrophy and deafness b. mental retardation, hypercalcemia, elfin facies, supravalvular aortic stenosis c. polyostotic fibrous dysplasia, café au lait spots, precocious puberty d. short stature, hypocalcemia, subcutaneous calcifications, obesity and short 4th metacarpals Answer Key 1. c 2.c 3. d 4. d 5. a. 6. c 7. d 8. a 9. c 10. c 11. b 12. a 13. c 14. a (also known as DIDMOAD b is William’s Syndrome c. McCune Albright d. Albright hereditary osteodystrophy(pesudophypoparathyroid)