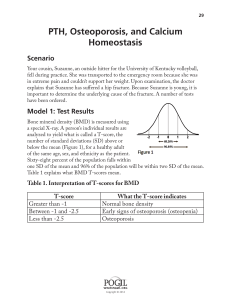
Gland Hormone Action Pineal Melatonin Circadian Rhythm Anterior Pituitary GH Cell Growth **More info in Table 61-2 p.1258(in old Med-Surg book) Posterior Pituitary ADH Water Balance Thyroid T3/T4 Metabolism (speeds up) *Results in an increase in oxygen use and heat production* Calcitonin Lowers Blood Calcium and Phosphorus (Calcium enters the bone and exits the blood) Nutrition aspect: Intake of protein and iodine needed to produce thyroid hormone Side note: ↑ Serum Ca=Calcitonin get to work! ↓Serum Ca= Block Calcitonin Parathyroid Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) Nutrition aspect: Vitamin D needed to help with function Raises blood Calcium; Increases bone resorption (Calcium exits the bone and enters the blood) Side note: ↑Serum Ca=Block PTH ↓Serum Ca= PTH do your thing! p.1260 (more info in Parathyroid Glands section in old book) Pancreas Insulin (secreted by beta cells) Lowers blood sugar (enhances glucose movement across cell membranes and into cells of many tissues) Adrenal Cortex (Think covering NOT core) Adrenal Medulla (Think Middle/Core) Glucagon (secreted by alpha cells) Raises blood sugar (triggered by decreased blood sugar levels) Somatostatin (secreted by delta cells Inhibits release of Insulin and Glucagon Glucocorticoids (Cortisol) Affects: • The body’s response to stress. • Carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism. • Emotional stability • Immune function • Na+ and H20 balance Mineralocorticoids (Aldosterone) Maintains ECF volume. (Promotes Na+ and H20 reabsorption and K+ excretion in the kidney tubules) Catecholamines (Epinephrine and Norepinephrine) “Fight or flight” Picture in PPT on p.5 Ovary Estrogen Female sex characteristics Testes Testosterone Male sex characteristics