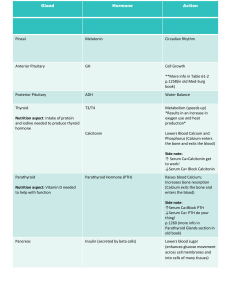
Parathyroid Disorders CBL Dr. Muhammad Imran FCPS, FRCS, MCPS-HPE Learning Objectives • Define hyperparathyroidism • Discuss different types of hyperparathyroidism • Describe investigations in a patient with hyperparathyroidism • Plan management of a patient with hyperparathyroidism • Discuss management of hypoparathyroidism Case-1 A 45-year-old female is referred to surgical OPD from medical outpatient department with the investigations; Serum calcium 11.2 mg/dl(Normal range 8.6 and 10.2 mg/dl) Parathyroid hormone level is 300 pg/ ml (normal range 1065 pg/ ml). Neck ultrasound: picture is shown; Her presenting complaints, in medical OPD, were psychological disturbances off and on and vague pain in legs Questions • • • • • • What is your provisional diagnosis? What is differential diagnosis? What are clinical presentations of this disease? How can you localize this disease with investigations? What should be the management plan? What are known complications of treatment? Provisional Diagnosis • Primary hyperparathyroidism Differential Diagnoses of Hypercalcemia History • Most patients are asymptomatic • Moans (CNS) • Stones (renal) • Abdominal groans • Bones (pains and tumors (Osteitis fibrosa cystica) • Family history (MEN?) Physical Examination Think about malignancy • Palpation of a parathyroid Adenoma Investigations • Electrolytes • Albumin - for corrected serum calcium (CSC) • CSC=[((4-patient albumin) * 0.8) + patient calcium] • PTH • PTH-related peptide • 24-hours urine calcium For familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia Neck Imaging (Ultrasonography) Technetium 99m Sestamibi Most sensitive Other Investigations (for persistent or recurrent hyperparathyroidism) • CT especially 4D-CT • MRI • Selective venous sampling Treatment Surgery Targeted approach Conventional approach Complications Case-2 A 62-year-male was admitted in nephrology unit for dialysis and management of electrolyte. His investigations reveal; Serum calcium 7.9 mg/dl(Normal range 8.6 and 10.2 mg/dl) Parathyroid hormone level is 150 pg/ ml (normal range 1065 pg/ ml) Questions • What is your provisional diagnosis? • How the management would be different from case-1? Provisional diagnosis • Secondary hyperparathyroidism Management • Initially conservative • Surgery in persistent cases • Total parathroidectomy with or without autotransplantation of 50 mg parathyroid tissue Case-3 A 19-year-old female, after total thyroidectomy, develops paresthesia in her fingers. Her serum calcium level is 7.2 mg/ dl on first postoperative day. Questions • • • • What is your diagnosis? What are different signs for hypocalcemia? What is significance of surgical anatomy? How will you manage this case? Diagnosis • Hypoparathroidism (postoperative complication) Signs of hypoparathyroidism Chvostek Trousseau Surgical anatomy • Inferior parathyroid and thymus from 3rd pouch • Superior parathyroid from 4th pouch • Vascular supply is important (Inf. thyroid) • Position is variable esp. inf. Parathyroid Management • 10ml of 10% Calcium gluconate IV • Oral calcium and Vit D Questions? You are able to; • Define hyperparathyroidism • Discuss different types of hyperparathyroidism • Describe investigations in a patient with hyperparathyroidism • Plan management in a patient with hyperparathyroidism • Discuss management of hypothyroidism Thank you