Foundations of Civilization
advertisement

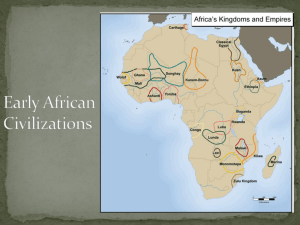
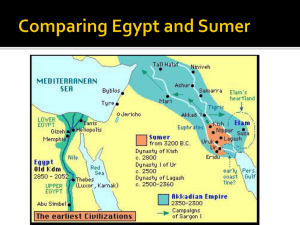
Foundations of Civilization The origins, development, and achievements of early human beings will influence the establishment of civilization. The Peopling of the World 2 million BC 8000 BC 3000 BC •Hunting-Gathering Bands •Growth of Villages •Rise of Cities Hunting-Gathering Bands Key Achievements: • Invention of tools • Mastery over fire • Development of language • Creation of art Neolithic Revolution Far-reaching changes in human life resulting from the beginning of farming One of the great breakthroughs in history Growth of Villages Key Achievements: • Breakthroughs in farming technology • Development of agriculture • Domestication of animals • Food surpluses Rise of Cities Key Achievements: • • • • Specialized workers Record keeping Complex institutions Advanced technology Culture The way of life of a group of people Includes: • Common practices • Clothing, food, sports, social customs • Shard understandings • Language, symbols, values, religious beliefs • Social Organization • Family, class structure, economic system, view of authority Culture is learned: • Observation and imitation • Direct teaching (spoken or written language) After the Neolithic Revolution shifted humans from nomadic to more sedentary life, early peoples organized their societies and built advanced civilizations. Characteristics of Civilizations Advanced Cities • Centers of political, economic, and religious life Specialized Workers • Food surpluses allowed people to specialize in jobs outside of agriculture • Artisans, traders, soldiers Complex Institutions • Law codes, religion, economy • Organized, untied, and helped civilizations to prosper Record Keeping and Writing • Record laws, write down religious dates and rituals, record transactions Advanced Technology • Metals, pottery, calendars Sumer Environment: • Tigris and Euphrates flooding unpredictable • No natural barriers • Limited natural resources Sumer Power and Authority: • Independent city-states governed by monarchs • City-states united into first empires Sumer Science and Technology: • Cuneiform • Irrigation • Bronze • Wheel, sail, plow Egypt Environment: • Nile flooding predictable • Natural barriers: deserts • Nile and easy transportation link Egypt Power and Authority: • Pharaohs rule kingdom as gods • Pharaohs built pyramids Egypt Science and Technology: • Hieroglyphics • Pyramids • Mathematics, geometry • Medicine Indus Valley Environment: • Indus flooding unpredictable • Natural barriers: mountains, deserts • Monsoon winds Indus Valley Power and Authority: • Strong centralized government • Planned cities Indus Valley Science and Technology: • Writing (not yet deciphered) • Cities built on precise grid • Plumbing and sewage systems China Environment: • Huang He flooding unpredictable • Natural barriers: mountains, deserts • Geographically isolated China Power and Authority: • Community and family important • Sharp social divisions • Mandate of Heaven • Dynastic Cycle China Science and Technology: • Writing • Silk • Coined money • Cast iron Migration and trade spread goods and cultural ideas throughout the ancient world. Indo-European Migrations Three major religions develop and spread as people migrated. Hinduism Buddhism Judaism Hinduism Number of Gods Many gods, all faces of Brahman Holy Books Vedas; Upanishads, Mahabharata, and others Moral Law Karma Leaders Brahmins Final Goal Moksha Buddhism Number of Gods Originally, no gods Holy Books Books on the teachings and life of the Buddha Moral Law Eightfold Path Leaders Monks Final Goal Enlightenment, Nirvana Judaism Number of Gods One God Holy Books The Torah and other books of the Hebrew Bible Moral Law Ten Commandments Leaders Priests, judges, kings, prophets Final Goal A moral life through obedience to God’s law Seafaring Trade • • • • Mediterranean Sea- Minoans and Phoenicians South and East Asia Land routes connect to Central Asia Trade networks ensured the exchange of products and information- CULTURAL DIFFUSION First Age of Empires The first large empires develop in Africa and Asia between 1570 BC and 200 BC Egypt (1570 – 1075 BC) • Pharaohs set up a professional army • Pharaohs invaded territories in Africa and Southwest Asia • Egypt drew vast wealth from the lands it controlled Nubia (751 BC – 350 AD) • Nubia and Egypt interacted and spread their culture through trade • The kings of Nubia conquered Egypt and maintained the Egyptian way of life • Nubia established trade among Africa, Arabia, and India Assyria (850-612 BC) • Assyria used a sophisticated military organization to conquer an empire • The empire engaged in brutal treatment of its conquered peoples • Kings used harsh taxes to control conquered peoples Persia (550-330 BC) • Persian kings were tolerant • Kings permitted a high degree of local self-government • The empire was divided into 20 provinces China (221-202 BC) • Ethical systems laid the groundwork for a strong central government • The Qin Dynasty defeated invaders, crushed internal resistance, and united China • China initiated a sweeping program of centralization