Cardiovascular System Defined Gross Anatomy of the Heart Operation of Heart Valves
advertisement
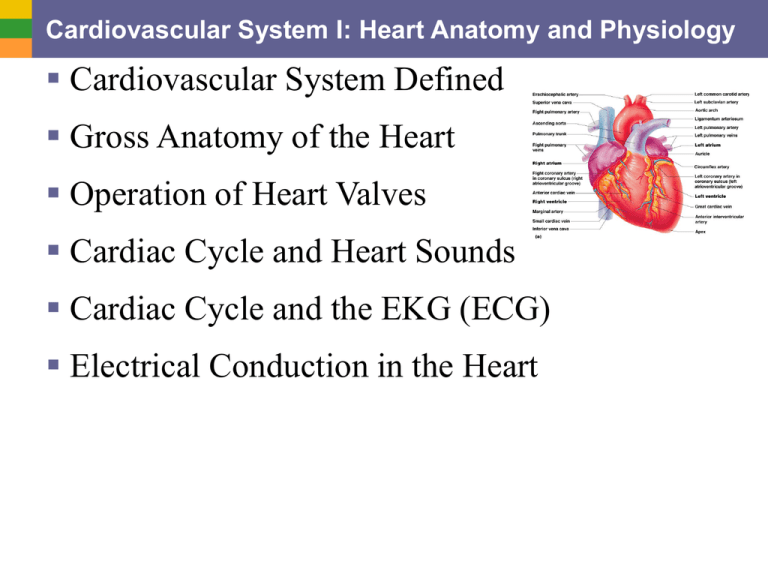
Cardiovascular System I: Heart Anatomy and Physiology Cardiovascular System Defined Gross Anatomy of the Heart Operation of Heart Valves Cardiac Cycle and Heart Sounds Cardiac Cycle and the EKG (ECG) Electrical Conduction in the Heart The Cardiovascular System Defined What it is: • A closed system of the heart and blood vessels o The heart pumps blood o Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body Function: • Deliver oxygen and nutrients and to remove carbon dioxide and other waste products Heart Gross Anatomy • Location: Mediastinum of the thorax • Size: As big as your fist • Serous Membrane Coverings: 1. Epicardium (= visceral pericardium) innermost 2. Parietal pericardium outermost 3. Mediastinal pleura outside that The Heart Wall: Three Layers Visceral Parietal Myocardium Endocardium Pericardium Pericardium (Epicardium) Parietal = visceral pericardium Exception: In the heart layers, peri- is outside of epi- Corornal Section of Human Heart Operation of Heart Valves AV valves Semilunar valves Stenotic and Regurgitant Valve Conditions Heart sounds movie online Flow of Blood Through the Heart Coronary Circulation: Blood Feeding the Heart Blockage of these vescles causes ischemia (lack of O2), causing muscle death (myocardio infarct), and chest pain (angina pectoris) Posterior View of Real Heart Auscultation of Heart Sounds Sounds 1 PCG: Phonocardiograph lub dup “S1” “S2” Split S1 Heart sound talk Auscultation Split S2 The Heart: Conduction System Intrinsic conduction system (nodal system) • Heart muscle cells contract, without nerve impulses, in a regular, continuous way Special tissue sets the pace 1. Sinoatrial node a. Pacemaker 2. Atrioventricular node 3. Atrioventricular bundle 4. Bundle branches 5. Purkinje fibers Contraction is initiated by the sinoatrial node Sequential stimulation occurs at other autorhythmic cells Exterior conduction Pacemaker with electrode in right ventricle Filling of Heart Chambers – the Cardiac Cycle 1. Atria contract simultaneously 2. Atria relax, then ventricles contract Systole = contraction (can be subdivided into atrial and ventricular contraction but otherwise refers to ventricular systole) Diastole = relaxation (ventricular) Figure 11.6 Cardiac Cycle and Electrocardiography P Q R S T U Note that an ECG does not show actual contractions but excitation and depolarizations Cardiac cycle – events of one complete heart beat • Mid-to-late diastole – blood flows into ventricles • Ventricular systole – blood pressure builds before ventricle contracts, pushing out blood • Early diastole – atria finish re-filling, ventricular pressure is low Pressure, ECG, and Heart online EKG, Heart contractions, conduction online Heart Voltages and the ECG Arrhythmias Heart block Hookups for the ECG