The Cardiac Cycle
advertisement

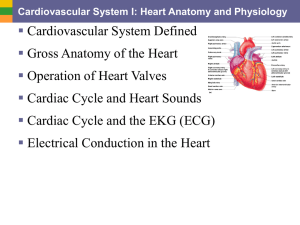
Cardiac Cycle & Cardiac Conduction Catalyst #2 • What is the outer covering of the heart called? • What cavity is the heart in? • What are the functions of the cardiovascular system? 13 - 2 The cardiac cycle The left and right sides of the heart contract together in a coordinated fashion Systole – contraction Diastole – relaxation Ventricular Systole • Ventricles contract to expel blood • Atria are in diastole during ventricular systole, filling with blood • Semilunar valves are opened, while AV valves are closed Ventricular Diastole • Ventricles are relaxed, filling with blood • Ventricles are 70% full before atria contract • Atrial systole pushes the remaining 30% of blood into ventricles • AV valves are opened while semilunar valves are closed Heart Sounds The heart valves produce a distinct sound as they close, which can be heard through a stethoscope. Lubb-Dupp • Lubb = sound of AV valves closing • Occurs during ventricular systole • Dupp = sound of semilunar valve closing • Occurs during ventricular diastole murmur = abnormal sound from the cusps not closing completely Heart Sounds - Ausculation Aortic valve (A) heard at 2nd intercostal space, right of the sternum 1 Pulmonary valve (P) heard at 2nd intercostal space, left of the sternum 2 3 4 Tricuspid Valve (T) heard at 5th intercostal space, either right or left of the sternum 5 6 7 Mitral Valve (M) heard at 5th intercostal space, below left nipple 8 9 10 Image from Grant’s Atlas of Anatomy. Each heart valve is indicated by a colored oval and the area of auscultation of the valve is indicated as a circle of the same color containing the first letter of the valve name. Cardiac Conduction of the Heart The heart is autorhythmic: • Specialized cardiac tissue initiate and distribute electrical impulses that generate heart contractions. Syncytium – mass of interconnected cells that function as a unit • Intercalated discs allow cardiac muscles to contract as a syncytium • Atrial Syncytium – Left and right atria contract together • Ventricular Syncytium – Left and right ventricles contract together Cardiac Conduction of the Heart Sinoatrial (SA) node • Pacemaker of heart • Initiates atrial syncytium • Fires 80 impulses per minute • Parasympathetic inhibition keeps heart rate at about 72 beats per minute Junctional Fibers • Conduct impulses towards both atria and towards AV node Figure 15.18 Illustrates the cardiac conduction system. Cardiac Conduction of the Heart Atrioventricular (AV) node • Located within inferior wall of interatrial septum • Provides a junction between atrial and ventricular syncytia AV Bundle (Bundle of His) • Only known conduction pathway between atria and ventricles • Divides into left and right bundle branches Figure 15.18 Illustrates the cardiac conduction system. Cardiac Conduction of the Heart Bundle Branches (Left and Right) • Runs down in left and right ventricles along either side of interventricular septum • Gives rise to Purkinje Fibers Purkinje Fibers • Carries impulses to ventricular myocardium and papillary muscles • Initiates ventricular syncytium at apex of heart Figure 15.19 Summarizes the cardiac conduction system Figure 15.20 Muscle fibers of the ventricles are whorled shape, which increases the blood output during ventricular systole. End of Section 2, Chapter 15 video • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7K2icszd xQc