Heart Physiology: Function, Rate, Sounds, and Circulation
advertisement

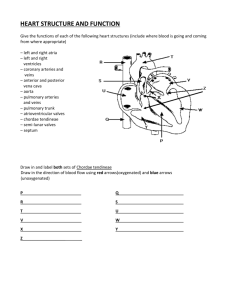
Physiology of the heart The Heart as a Pump The ventricles serve as the force behind the pump. Specialized structures called intercalated disks allow cells to beat in synchrony. This coordinated heartbeat is call interstitial syncytium and makes the heart a more effective pump. What is the definition of a heartbeat? Heartbeat Definition: a single sequence of atrial contraction followed by ventricular contraction. Contraction:the process in which a muscle becomes or is made shorter and tighter. Heartbeat vs Pulse Heart rate is the number of times per minute that the heart contracts - the number of heart beats per minute. Pulse is the mechanical movement of blood flow through the capillaries caused by the contractions of the heart per minute. The number of heartbeats per minute should be the same the pulse count True False Heartbeat ▪ Normal rate: 60-100 What affects the rate ? ● ● ● ● Age Fitness level Presence of certain medical conditions Some drugs including caffeine and nicotine. 7 Heart sounds ▪ Called S1 LUB and S2 DUB ▪ S1 is the closing of AV (Mitral and Tricuspid) valves at the start of ventricular systole ▪ S2 is the closing of the semilunar (Aortic and Pulmonic) valves at the end of ventricular systole 8 Some terms to know ▪ Slow heartbeat: bradycardia ▪ Fast heartbeat: tachycardia ▪ Systole: the highest blood pressure that occurs as the ventricles contract ▪ Diastole: the blood pressure when ventricles are relaxed and filling. A young man has a pulse of 120. He is suffering from Action Potential Cells have a negative membrane potential. A signal from a nerve allow ions to enter the cell changing the potential and forcing the cell to contract. Repolarization=Relaxation Depolarization = Contraction “EKG” (or ECG, electrocardiogram) ▪ Electrical depolarization is recorded on the body surface by up to 12 leads ▪ Pattern analyzed in each lead P wave=atrial depolarization QRS=ventricular depolarization T wave=ventricular 12 repolarization Label diagram in your notebook Electrical conduction system: The system is composed of specialized cardiac muscle cells that carry impulses throughout the heart musculature. These cells signal the chambers to contract in the proper sequence. (Explanation in next slides) 14 Parts of the Conduction system SA node (sinoatrial) -Located in the upper wall of Right Atrium -Sets heart rate: 70-80 -Is the “natural” pacemaker AV node (atrioventricular) -Located in the lower wall of the right atrium -It receives the impulse from SA node as it moves toward the right ventricle. 15 Conduction continued AV bundle (bundle of His) ▪ Found in the interventricular septum ▪ The AV bundle divides into right and left bundle branches which deliver the impulse to the bottom of the heart. The Purkinje fibers complete the signal by spreading the impulse through the outer walls of the ventricles. 16 Right and left Bundle branches SA Node AV node Purkinjie Fibers Artificial Pacemaker 19 Coronary Circulation The heart has its very own blood vessels! The blood inside the heart does not supply the heart muscle. On the outside of the heart you see coronary vessels that supply the heart muscle. Myocardial infarction When the blood supply to the heart muscle is blocked, The tissue dies. This is what causes a heart attack another flow chart 23 Use to study 24 Starting from the outside… Pericardium (see next slide) Without most of pericardial 25 Coverings of the heart: pericardium ▪ 2 layers of pericardium ▪ Parietal layer of serous pericardium ▪ Visceral layer of serous pericardium = epicardium: on heart and is part of its wall (Between the layers is pericardial cavity) 26