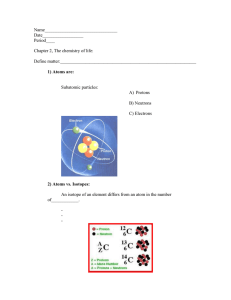
What is an atom? What three types of particles are... the atoms is each particle found?
advertisement

Biology 1406 Test I Study Guide Chemistry of Living Systems What is an atom? What three types of particles are commonly found in atoms? Where in the atoms is each particle found? Be familiar with concepts / terms such as: electrically neutral, atomic number, atomic weight, isotope, ion, cation, anion, electrolyte, electron donor, electron acceptor, acid, base, and buffer. What determines whether a particular atom is gold rather than silver, lead rather than carbon? What are the elements necessary to living systems? Which of these are the most common? How many electrons are typically found in orbitals (energy levels)? How many electrons are at various distances around an atom’s nucleus? What are valence electrons and why are they important? What sorts of bonds are commonly used in living system to combine atoms into molecules? How does each form? (i.e. sharing vs. transfer of electrons) How do polar and nonpolar covalent bonds differ from each other? What are hydrogen bonds? How do they differ fundamentally from both covalent and ionic bonds? What are solubility and dissociation? How do they differ from each other? What is a chemical reaction? What sorts can occur? (synthesis / anabolic, decomposition / catabolic) How does the energy needs differ between endergonic and exergonic chemical reactions? What are oxidation and reduction? What is an oxidation / reduction reaction? What sorts of factors affect the rate at which a reaction might run? How does each have an effect? What is activation energy and how can it determine whether a reaction will occur? (hint: think of how a pan of cake batter might or might not become a cake) What determines whether a particular chemical is ‘organic’? Know the definitions for both acid and base. What ion is common to all acids? What ion is common to all bases? 1 What is a buffer? What two ‘partner’ molecules make up a buffer system? What are some of the functions of water in the body? Know the four types of ‘biomolecules’ in living systems including lipids, carbohydrates, proteins and nucleic acids. For each of the four biomolecules know what monomer is used to make the polymer, how each is formed, some functions performed by each. 2