Chemistry of Life: Cells & Organization Notes
advertisement

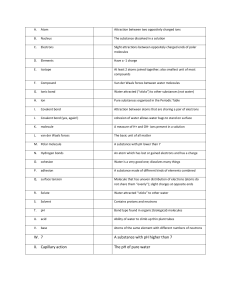
Unit 1: CELLS- Understanding the organization and building blocks of life NOTES: The Chemistry of Life. The Levels of Organization in Living Things Before we can study biology, we need to understand “what” living things are made of. An essential part of that is knowing how all living things are made-up. All living things demonstrate a similar pattern of organization that we refer to as the “Levels of Organization”. Levels of Organization 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 All living cells carry on many complicated cellular processes to ensure that living organisms remain “alive”. In order for you to understand living things, some knowledge of basic chemistry is necessary. This knowledge will be useful in helping you understand biology, as all organisms are chemical machines. Matter All matter is composed of one or more elements. Element: Definition: All known elements are organized by physical and chemical properties within the Periodic Table of the Elements. Understanding the Periodic Table of The Elements Each element displayed within the periodic table is physically different from the other 116 elements. The basic “unit” of the element is called the atom. These atoms are made up of 3 particles: 1. Protons: 2. Electrons: 3. Neutrons: Structure of the Atom The very center of the atom is called the nucleus. A. B. C. Surrounding the nucleus are the electrons. A. B. C. D. Electrons Atoms possess a great deal of energy in the form of chemical energy. A. B. When Atoms Combine: Chemical Bonds Atoms are highly reactive and interactive. A. B. 1. 2. Forming Molecules Molecules are able to form through the formation of chemical bonds. Definition: Molecules are chemically neutral. If they end up becoming positively or negatively charged, they are called an “ion”. This happens if they gain or lose electrons. 3 Types of Bonds 1. Covalent bond: 2. Ionic bond: 3. Hydrogen bond: Chemical Reactions The process by which elements react to form new compounds requires a chemical change. A. B. C. THE WRAP UP: How Does All of This Connect? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7.