LIPID (FAT) NOTES
advertisement

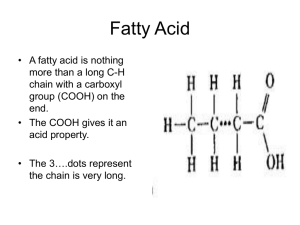
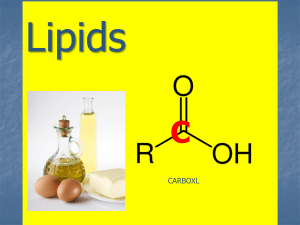
LIPID (FAT) NOTES Lipids Waxy or oily compounds that store energy in their bonds Elements in lipids – carbon, hydrogen & oxygen Examples – fats, oils & waxes Functions in the body Long-term energy storage Insulation Forms the protective membrane that surrounds each cell Some used as chemical messengers Types of Lipids – fats that hold all the hydrogen that molecule can hold Examples: shortening & butter Saturated H H H H–C–C–C–O–H H H H Types of Lipids, cont. – fats that have some spaces left in the molecule for hydrogen Examples: oils Unsaturated H C=C=C–O–H H H Building Blocks Fatty acids – the building blocks of fats (lipids) Food Energy 1 gram of lipids (fat) is 9 calories Healthy Living Fact: •Your body needs some fat. •Read the nutrition labels & choose unsaturated fats instead of saturated or trans fats