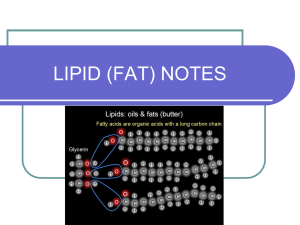
Lipids C CARBOXL Fats and oils are part of a large group called Lipids. Lipids are a family of chemical compounds that are a main component in every living cell. Lipids 1. 2. 3. We get lipids by eating plants and animals that eat plants. Plants make lipids by adding small molecules together. Glycerol + C+C+C+C+C+C+C+C+C++++ Lipids Main Functions 1) Fuel for the body – 9 kcalories/gram 2) Keep the body warm: Homeostasis Insulation under skin keeps body at 98*.) Cushions around vital organs. 3.) Cell Membranes 4.) Keep hair and skin supple. Phospholipids A. Dissolve in fat & water B. Emulsifiers - Hold water & lipids together: C. Make phospholipids bi-layer in all cells +4 Structure Composed of of Lipids CHO FATTY ACIDS: Carbon chains w/Hydrogen + carboxyl group at one end. CARBOXYL GROUP R = rest of molecule Acetic Acid is the simplest fatty acid with 2 carbons. Draw the diagram of it here. Circle the carboxyl group of your acetic acid. Saturated Fat IT IS COMPLETE FULL OR SATURATED WITH HYDROGEN. (You can’t get any more attached.) They are found in foods from animals. Unsaturated Fat They have some double bonds & can hold more hydrogen. Two Kinds of Unsaturated Fats: Monounsaturated Fat: Have 1 double bond Found in OLIVE OIL, and other plant oils Oleic Acid – 1 double bond Poly-unsaturated Fats Have double bonds Found in plant OILS Linoleic Acid – 2 double bonds Linolenic Acid – 3 double bonds Lipids and proteins are needed for growth and repair of the body. It is ESSENTIAL we get C H O from food For every cell in our bodies. Sources: Oils in vegetables, grains, nuts, seeds and soybeans Fats and cholesterol in meat from animals Triglycerides 1. 2. 3. Largest class of lipids 90%+ more of fats in the body Include nearly all of the fats & oils Triglycerides make up 90% in our food. They are made of a glycerol head and 3 long tails of saturated and unsaturated lipids. Show What You Know 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. YOYO: List 3 oils and 3 fats SB: Add two more to your list YOYO: What is the sources of most oils? SB Share your list and add 3 sources of most fats? Draw a picture of saturated fats Draw a picture of unsaturated fats Draw a picture of polyunsaturated fat Draw a picture of triglycerides. Check your drawings with your SB. Lipids in your diet become lipids in your body. Fats are absorbed by the villa in the small intestine. Sterols A. Cholesterol is a sterol. C27H45OH. C+C+C+C+ B. Found in Cell’s membrane. C. Arteries Cholesterol Why is Cholesterol necessary? Produces vitamin D Cell Membranes Hormones: Messengers Estrogen Cortisone Testosterone Insulin The liver makes all the cholesterol the body needs. Extra Cholesterol may lead to PLAQUE: sterols with calcium and smooth muscle cells. Plaque lodges in artery walls reducing blood flow which may lead to death. You do not need to eat foods with cholesterol. Foods High in Cholesterol Eggs, Red Meat, Sea Food, Butter, Bacon, Hot Dogs, Cookies, Fast Food, Cheese, Pie Crust, Pepperoni, Hot Pockets Vegetables low cholesterol in the body! The heart has to work harder to push blood through clogged arteries It raises blood pressure. Atherosclerosis The hardening of the arteries: The arteries become less flexible. May lead to early death Transfats are Manmade Fast Foods Margarine Baked Foods Processed Foods/Meats Clog up your arteries faster than every other kind of lipid. 1. YOYO What are 3 sources of transfats? 2. SB add 3 sources of transfats to your list. 3. 3. Share with the class.