Section III (Colligative Property)
advertisement

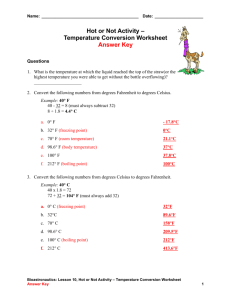
49 COLLIGATIVE PROPERTY Section III COLLIGATIVE PROPERTY LAW It was found that adding a solute to a solvent lowers the freezing point and the vapor pressure but elevates the boiling point of the pure solvent. The lowering of the freezing point and vapor pressure and the elevation of the boiling point of the solvent depend on the number of solute particles added and not on the type of particles added. It was found that adding 1 mole of a non-electrolyte lowers the freezing point of 1000 g of water by 1.86C. 1.86C is known as the molal freezing point constant for water. Each solvent has its own molal freezing point constant, given a symbol Kf, for example, for benzene Kf is 4.9C. It was also found that 1 mole of a non-volatile non-electrolyte elevates the boiling point of 1000 g of water by .52C. .52C is the Kb, known as the molal boiling point constant for water. If the lowering of the freezing point or the elevation of the boiling point of a solution is known then it is possible to calculate the molality of the solution using Eq. 7a or 7b. Eq. 7a m= f . p. molal f. p. constant Eq. 7b m= b. p. molal b. p. constant For example, the freezing point of a sugar solution was -.93C. Calculate the molality of the solution. SOLUTION using Eq. 7a m= .93 = .5 186 . It is possible to use the lowering of the freezing point or the elevation of the boiling point to calculate the molecular weight of an unknown non-electrolyte by using Eq. 6 and 7a or 6 and 7b. EXAMPLE 1 10 g of an unknown non-electrolyte dissolved in 150 g of water lowered the f.p. of water 1.2C. Calculate the molecular weight of the substance. Given Kf = 1.86 SOLUTION Using Eq. 7, Calculate the m m= 12 . = .64 186 . 50 Substitute the value in Eq. 6 10 g = (.64)(150g of solvent)(mol. wt.) 1000 Solving the equation for the molecular weight m.w. = 10 1000 = 104 .64 150 EXAMPLE 2 The molecular weight of non-electrolyte is 58. What will be the boiling point of a solution containing 24 g of the non-electrolyte dissolved in 600 g of water. Given Kb = .52C SOLUTION 24 1000 24 .69 Molality of solution is equal to 58 600 58 600 1000 We know that m = bp kb Therefore, bp = .52 .69 = .35C Therefore, the boiling point of the solution is 100C + .35C = 100.35C.