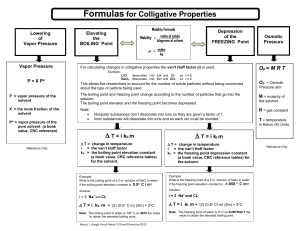
instructions on how to calculate freezing point and boiling point
advertisement

To calculate freezing point and boiling point; 1. Convert grams of solute to moles of solute and then molality of the solution. 2. ID the solute to number of particles. Ex: CaCl 2= 3 particles C6H12O6= 1 particle 3. Multiply the number of particles by the molality calculated #1 to get the new molality 4. Plug into formula: a. Freezing delta t = Kf(of solvent) m (new molality) b. Boiling delta t = Kb (of solvent) m (new molality) 5. Old freezing point – delta t = new freezing point 6. Old boiling point + delta t = new boiling point When a solute is added to a pure solvent the freezing point is lowered and the boiling point of the solvent is elevated. To calculate molar mass work backwards. Step 5 or 6 goes step 4, and step 4 goes to three. In step 3 where you multiply by particles you will divide.