Chapter 18 Notes, part III
advertisement

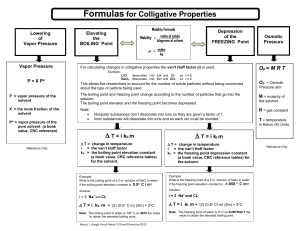
Chapter 18 Notes, part III Colligative Properties What are colligative properties? Properties that are only affected by the number of particles dissolved in a solvent. Ionic vs. Covalent in Colligative Properties As discussed before, when a salt dissolves in water it dissociates. This means there are more particles in a solution of a salt in comparison to a solution with a covalent compound (such as sugar). How many particles do the following break into: NaCl CaCl2 C6H12O6 H3PO4 CO2 KNO3 N2O Na2CO3 AlF3 C3H6O Be3N2 SO3 Three Colligative Properties Boiling Point Elevation Freezing Point Depression Vapor Pressure Boiling Point Elevation When a solute is added to a solution, the boiling point of the liquid is increased. It takes more kinetic energy to get the molecules out of the liquid phase and into the gas phase! Why is this? Freezing Point Depression When a solute is added the freezing point of a solvent is decreased. Why does this occur? Vapor Pressure There is a decrease in vapor pressure when a solute is added to a solvent. This is because the solvent’s particles are busy surrounding the solute, so less are free to escape into the air. Calculating Change in Boiling/Freezing Point The change in boiling point can be found using the formula: DTb=Kb x m For water, Kb=0.512oC/m The change in freezing point can be found using the formula: DTf=Kf x m For water, Kf=1.86oC/m Practice Problem #1 What temperature does a salt solution boil at if 95.5g of NaCl has been added to 1.5kg of water? Practice Problem #2 At what temperature does a solution freeze if it is made by adding 52.2g of MgCl2 to 1127g of water? Practice Problem #3 What is the molar mass of a sugar if when 235.8g are dissolved into 515g of water, the boiling point is 101.3oC? Practice Problem #4 What is the molar mass of a salt that breaks into two parts, if when 122.5g are dissolved into 495g of water, the boiling point is 103.1oC?