Colligative Properties of Solutions
advertisement

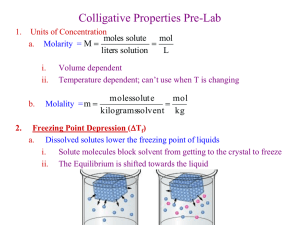
Solutions Colligative Properties of Solutions Objectives 1. Describe the colligative properties of a solution. 2. Calculate freezing point depression and boiling point elevation for solutions Colligative Properties • A property that depends on the concentration of solute particles but not on the identity of the solute. Vapor Pressure Lowering • As the concentration of a solute increases, the concentration of the solvent particles at the surface of a liquid decreases. This causes the vapor pressure to be lower. • A 1.0 m solution of glucose (C6H12O6) lowers the vapor pressure to the same extent as a 1.0 m solution of sucrose (C12H22O11) Freezing Point Depression Freezing Point Depression (Δtf): the difference between the freezing point of a pure solvent and a solution of a solute in the same solvent. Δtf = Kfm Kf = molal freezing point constant in oC/m m = molality Sample Problem 1. What is the freezing point depression of water in a solution of 17.1 g of sucrose (C12H22O11) and 200. g of water? What is the actual freezing point of water. Water has a Molal F.P. constant of -1.86 oC/m. Sample Problem 2. A water solution containing an unknown quantity of a non-electrolyte solute is found to have a freezing point of -0.23 oC. What is the molal concentration of the solution? Sample Problems 1. Determine the freezing point of a water solution of fructose (C6H12O6) made by dissolving 58.0 g of fructose in 185 g of water. -3.24oC 2. Calculate the molality of a solution of 39.2 g of urea, H2NCONH2, in 485 g of pure acetic acid. Determine the freezing point of this solution. For acetic acid: Normal f.p. = 16.6oC Kf = -3.90 oC/m 1.35 m, 11.3 oC Sample Problems 1. What is the expected change in the freezing point of water in a solution of 62.5 g of barium nitrate, Ba(NO3)2, in 1.00 kg of water. Sample Problems 1. What is the expected freezing point depression for a solution that contains 2.0 mol of magnesium sulfate dissolved in 1.0 kg of water? -7.4oC 2. A water solution contains 42.9 g of calcium nitrate dissolved in 500. g of water. Calculate the freezing point of the solution. -2.92oC Boiling Point Elevation Boiling Point Elevation (Δtb): the difference between the boiling point of a pure solvent and a solution of a solute in the same solvent. Δtb = Kbm Kf = molal boiling point constant in oC/m m = molality Sample Problem A solution contains 50.0 g of sucrose, C12H22O11, a nonelectrolyte, dissolved in 500.0 g of water. What is the boiling point elevation? Sample Problems 1. What is the boiling point of a solution of 25.0 g of 2-butoxyethanol, HOCH2CH2OC4H9, in 68.7 g of ether? (For ether, ∆tb= 2.02oC/m) 40.8oC 2. What mass of glycerol, CH2OHCHOHCH2OH, must be dissolved in 1.00 x 103 g of water in order to have a boiling point of 104.5oC? 810g 3. What is the expected boiling point of a 1.70 m solution of sodium sulfate in water? 102.6oC