Review Sheet Filled Out
advertisement

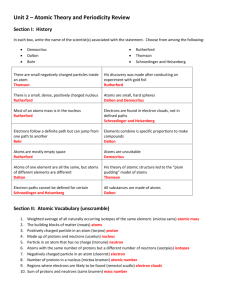
Review Sheet – Atoms and the Period Table Element Atomic Number # of Neutrons Magnesium Carbon Xenon Rubidium Aluminum Sulfur 12 6 54 37 13 16 12 6 77 48 14 16 # of Energy Levels 3 2 5 5 3 3 1. Find the average atomic mass of Lithium: Li-6 7.42% Li-7 92.58% 6.9258 amu = 6.93 amu 2. Draw a Lewis Dot Diagram of the following atoms. Cl 3. +2 -4 0 +1 +3 -2 Ba Draw a Bohr Model of the following atoms. Too hard to do on the computer. S 4. Pb Oxidation # Al Na Give the oxidation numbers for the following ions: P-3 O-2 Ar none Al+3 Sn+4 Be+2 5. List the number of facts you know about electrons. Electrons closest to the nucleus have the least amount of energy Electrons farthest away from the nucleus have the most energy – valence e Have a negative charge Have insignificant mass and volume Reside in the 99.996% of the atom outside the nucleus Can’t tell where an electron is at any moment in time – the uncertainty principle There’s more – the list could be long! 6. What is Dalton’s Atomic Theory? All matter is made of atoms that cannot be divided, created, or destroyed. During a chemical reaction, atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element. Atoms of one element are identical to each other but different from atoms of another element. Atoms combine in specific ratios – even, whole number ratios. 7. Write the Orbital Notation and the Electron Configuration for: After Argon, you can use the noble gas configuration for the electron configuration and orbital notation like I did with Barium. I just did Lead the long way to show you what it would look like. This is electron configuration. The ON would be too hard to do on the computer. Iron 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6 Argon 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 Oxygen 1s2 2s2 2p4 Lead 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p6 6s2 6f14 5d10 6p2 Barium Xe 6s2 I. STATES OF MATTER 1. Kinetic Molecular Theory 3. thermal energy 5. solid 7. liquid 9. gas 11. plasma 13. diffusion 15. sublimation 17. Heat of Fusion II. 1. 3. 5. 7. 9. 11. 13. 15. PROPERTIES OF MATTER density hardness brittleness tensile strength buoyancy Boyle’s Law Gay-Lussac’s Law ductile 2. temperature 4. heat 6. allotrope 8. phase change diagram 10. evaporation 12. boiling point 14. Heat of vaporization 16. Melting point 2. viscosity 4. elasticity 6. malleability 8. fluids 10. Archimedes Principle 12. Charles’ Law 14. Combined Gas Law 16. pressure Calculations: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Density Boyle’s Law Charles Law Gay-Lussac’s Law Combined Gas Law D = mass/volume P1V1 = P2V2 V1/T1 = V2/T2 P1/T1 = P2/T2 P1V1 = P2V2 T1 T2 3 7. 1g H2O - 1mL H2O = 1 cm H2O 8. 1 g/mL = 1 g/cm3 9. How to convert between area units and volume units Things to Know: 1. 2. 3. The 4 states of matter and the characteristics of each How temperature affects density How temperature affects the volume of a gas 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. How pressure affects the volume of a gas How pressure affects temperature of a gas How pressure is created Phase Change Diagram Kinetic Molecular Theory Rules for Gas Laws – STP, converting oC to K, reporting answer in significant digits and in scientific notation History of the Atomic Model The dry ice and pipette activity Electron Configuration and Orbital Notation Oxidation Numbers How to calculate average atomic mas How to determine the number of protons, neutrons, electrons Rutherford’s Gold Foil Experiment Significant Digits Bohr model for the representative elements Lewis Dot diagram for elements