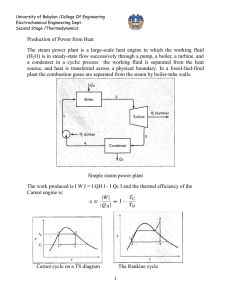
University of Babylon /College Of Engineering Electrochemical Engineering Dept. Second Stage /Thermodynamics
advertisement
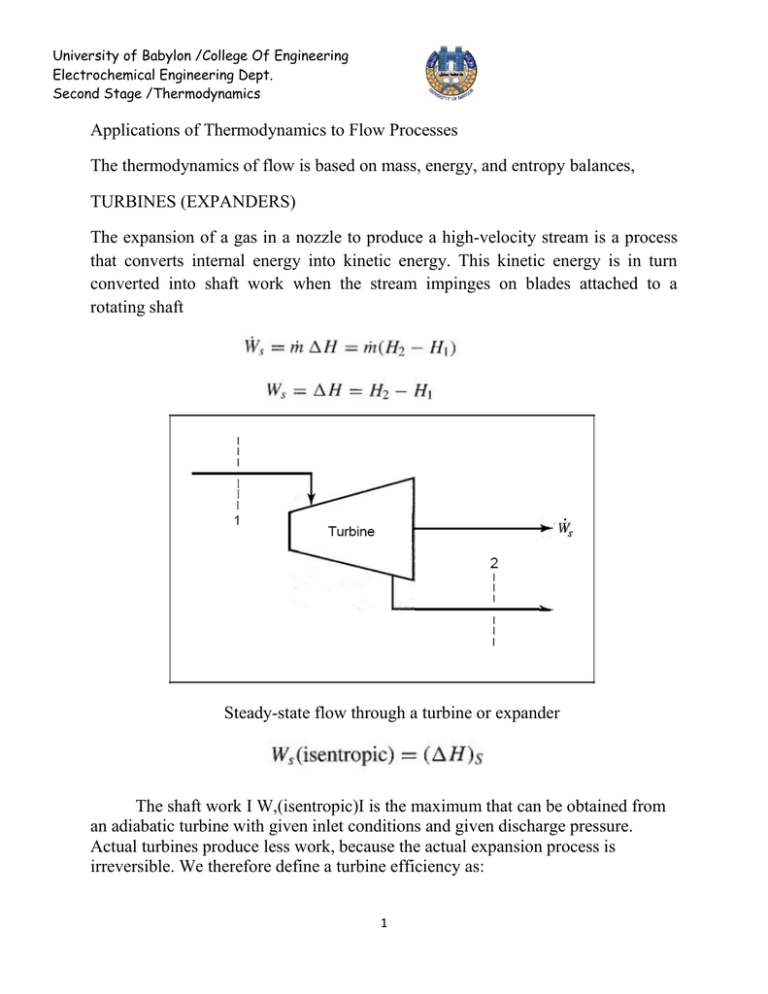
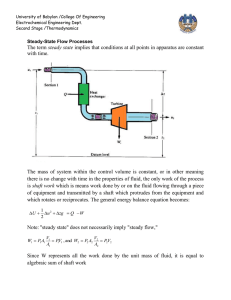
University of Babylon /College Of Engineering Electrochemical Engineering Dept. Second Stage /Thermodynamics Applications of Thermodynamics to Flow Processes The thermodynamics of flow is based on mass, energy, and entropy balances, TURBINES (EXPANDERS) The expansion of a gas in a nozzle to produce a high-velocity stream is a process that converts internal energy into kinetic energy. This kinetic energy is in turn converted into shaft work when the stream impinges on blades attached to a rotating shaft Steady-state flow through a turbine or expander The shaft work I W,(isentropic)I is the maximum that can be obtained from an adiabatic turbine with given inlet conditions and given discharge pressure. Actual turbines produce less work, because the actual expansion process is irreversible. We therefore define a turbine efficiency as: 1 University of Babylon /College Of Engineering Electrochemical Engineering Dept. Second Stage /Thermodynamics Adiabatic expansion process in a turbine or expander Compressors The compression of gases may be accomplished in equipment with rotating blades (like a turbine operating in reverse) or in cylinders with reciprocating pistons. Rotary equipment is used for high-volume flow where the discharge pressure is not too high. For high pressures, reciprocating compressors are required. The energy equations are independent of the type of equipment; indeed, they are the same as for turbines or expanders, because here too potential- and kinetic-energy changes are presumed negligible. 2 University of Babylon /College Of Engineering Electrochemical Engineering Dept. Second Stage /Thermodynamics Steady-state compression process Compressor efficiencies are usually in the range of 0.7 to 0.8 . Adiabatic compression process 3