Structure 2 Review Worksheet 2007
advertisement

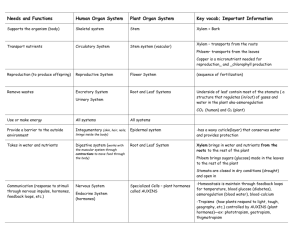
☞Structure 2 Review Worksheet 2007 ☜ 1. Which is of the following NOT a function of roots? A. Produce hormones B. Store food C. Anchor plant D. Absorb water and nutrients E. Protect the plant 2. Which is of the following NOT a common tap root? A. potatoes B. beets C. carrots D. radishes 3. Bacteria in the soil convert atmospheric nitrogen into a form that plants can use during the process of ____. A. nitrification B. denitrification C. nitrogen fixation D. ammonification E. none of these (NOT) 4. Lateral roots _____. A. protect apical meristems B. are for food storage C. are mainly to increase absorption D. always have a symbiotic relationship with bacteria E. grow in the air, not in soil 5. Root caps ___. A. protect apical meristems B. are for food storage C. are mainly to increase absorption D. always have a symbiotic relationship with bacteria E. grow in the air, not in soil 6. The function of the casparian strip is to__. A. channel water into vascular tissue B. increase surface area for absorption C. form a symbiotic relationship with fungi D. absorb water from the atmosphere E. anchor a plant in the soil 7. A node is __. A. a stem that is used for food storage B. the place where one or more leaves are attached to a stem C. the space on a stem between leaf attachments D. a stem with many fleshy leaves E. NOT 8. Stem growth in circumference takes place due to __ meristems. A. intercalary B. lateral C. apical D. medial E. terminal 9. Yearly increase in stem width occurs in ___. A. monocots 1 B. dicots 10. _____ is found at the center of a tree trunk. A. living xylem B. living phloem C. Sapwood D. Heartwood E. Cork 11. Which of the following is NOT a function of stems? A. hold leaves up to the sun B. transport nutrients up from the roots C. channel water into vascular tissue D. food storage in some plants 12. Which of the following is NOT true of sapwood? A. Grows wider from year to year B. Is light in color C. Is made of living xylem D. Is nearer to the outside than the inside of the tree E. Functions in transport of water and nutrients 13. In translocation, __. A. xylem moves sugars from leaves (source) to areas where they are stored (sink) B. xylem moves sugars from areas where they are stored (sink) to leaves (source) C. phloem moves sugars from leaves (source) to areas where they are stored (sink) D. sugars are moved to places they are needed by gravity E. sugars are moved due to adhesion and cohesion 14. The Pressure-Flow hypothesis explains___. A. how sugars are moved by xylem B. how water and nutrients move up the stem from roots D. how sugars from a source cell are pumped into sieve cells E. how plants perform gas exchange 15. The Cohesion-Adhesion Theory ___. A. involves food storage in the plant B. includes translocation, and transpiration C. causes phloem to move water and nutrients D. causes xylem to move water and nutrients E. does not occur in cacti 16. Excess water is released from leaves during the process of ___. A. Adhesion B. Nitrogen fixation C. Cohesion D. Transpiration E. Translocation 17. Which of the following best describes why water movement in xylem stops at night? A. Stomata are usually closed and transpiration stops B. Water is magnetically attracted to the sun C. No translocation occurs at night D. Stomata are normally open, so negative pressure prevents water movement E. Water clings to the sides of vascular tissue so much that water movement stops 2 18. The function of endosperm is __. A. to protect the embryo B. to prevent dehydration of the embryo C. to provide a food source for the embryo D. to absorb water for the embryo E. A and B 19. The function of the seed coat is__. A. to protect the embryo B. to prevent dehydration of the embryo C. to provide a food source for the embryo D. to absorb water for the embryo E. A and B 20. The function of a flower is __. A. Absorb nutrients B. Reproduction C. Absorb ultra-violet rays for photosynthesis D. Transport nutrients E. Perform photosynthesis Matching Place the letter of the best answer on the answer sheet. 21. grow near soil surface; grass has these 22. have a symbiotic relationship with fungi 23. large main root for food storage 24. for support; grow down from stem above soil 25. grow without soil, absorb water from air 26. underground stem with buds 27. upright, thickened underground stem 28. horizontal underground stem 29. large underground bud with many layers 30. Stigma 31. Filament 32. Petal 33. Sepal 34. Ovary 35. Style 36. Anther A. Tap roots B. Prop roots C. Aerial roots D. Fibrous roots E. Mycorrhizae A. Rhizome B. Tuber C. Bulb D. Corm A. supports stigma B. supports anther C. collects pollen D. releases pollen E. attracts pollinators F. protects flower bud G. contains eggs Short Answer 37. What is the function of a tap root? 38. What is turgor pressure? 39. Why do cacti have stomata closed during the day, but open at night? 40. Where are the stomata on a water lily pad (leaf)? Why? 3 Diagrams Label leaf cross-section by placing the letter of the best answer on the answer sheet. 41. spongy mesophyll 42. air space 43. cuticle 44. epidermis 45. palisade layer 46. stomata 47. vascular bundle(vein) A E F B C. D G Label these stem cross-sections by placing the letter of the best answer on the answer sheet. 48. dicot 49. monocot A B 4 Label these leaves by placing the letter of the best answer on the answer sheet. 50. simple leaf 51. compound leaf A B Label these leaves by placing the letter of the best answer on the answer sheet. 52. parallel venation 53. pinnate venation 54. palmate venation A. B. C. 5 Label these leaves by placing the letter of the best answer on the answer sheet. 55. serrate leaf margin 56. entire leaf margin 57. lobed leaf margin A. B. C. Label these flower parts by placing the letter of the best answer on the answer sheet. 58. stigma 59. anther 60. ovary 61. style 62. filament 63. petal A. B. C. D. E. F. 6