Name___________________________ Lecture Section__________________ Chemistry 331: Organic Chemistry
advertisement

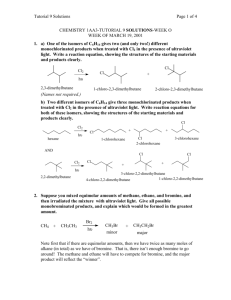
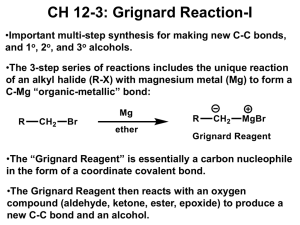
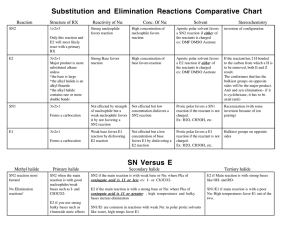
Name___________________________ Lecture Section__________________ Chemistry 331: Organic Chemistry Fall 2014, University of Delaware Prof. Donald Watson Problem Set 4 Due Beginning of Class 10/31/14 You may work in groups. Please write answers in the space below, for problems form the book, please attached them on separate sheet(s) of paper. Each student must turn in their own, handwritten answer set to get credit. Please write answers on this page. 1. Draw the chair conformations for the following molecules and state which is more stable. Please estimate the relative stabilities of each conformer. Do these differ from the simple additive effects of A-values? If so, why? 2. Draw the most stable conformation of this molecule, where all substituents on the ring are equatorial. 4. Fusidic acid is a steroid like microbial product that is extremely potent antibiotic with a broad spectrum of biological activity. (a) Locate all the rings in fusidic acid and describe their conformations (b) identify all ring fusions in the molecule as having wither cis or trans geometry. 5. Draw structural representations of each of the following molecules. a. (R)-3-Bromo-3-methylhexane b. (S)-1,1,2-Trimethylcyclopropane c. (1R,2R,3S)-1,2-Dichloro-3-ethylcyclohexane 6. Using your understanding of substitution transition states, explain why the SN2 reaction of trifluoromethyl iodide with butylamine does not work. I Me NH 2 + F F NO REACTION F 7. While Grignard reagents are versatile reagents, they are not often employed with simple alkyl halide electrophiles because they often give alkenes as the predominant product, as shown below. Explain this phenomenon. I + Me MgBr Me Me Me Me + Me 8. Explain why the Grignard reagent shown below would not be stable in solution. OH ClMg Me Me 9. Provide the products and the equilibrium constant for each of the following reactions. O Me N + Me K a= OH Me K a= O Me OH + Me S K a= Me Me OH Li + + H Cl K a= Me NH 2 10. For each of the following pairs of isomeric alkyl halides indicate which isomer is the more reactive in SN2 reactions. 11. Show how you might synthesize the following compounds from an alkyl halide and a nucleophile. Provide the starting materials and an arrow pushing mechanism. Also describe any changes in the 13C NMR for each compound compared to the starting alkyl halide.