CH 12-4: Performing a Grignard Synthesis-II
advertisement

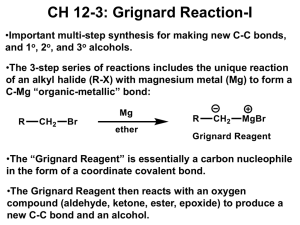
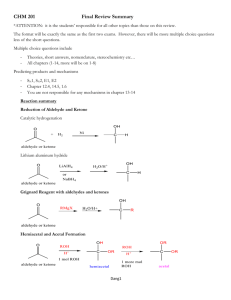
CH 12-4: Performing a Grignard Synthesis-II •Study the target molecule and the list of available reagents. •Locate the new bond in the target molecule and draw a “dot” on the alcohol carbon. •Is the target a 1o, 2o, or 3o alcohol? Do you need an aldehyde, ketone, ester or epoxide? If symmetrical alkyl groups at the alcohol carbon, then use an ester. •From the reagent list (stockroom) identify the reactants needed to make the target molecule. •Which reactant will you use to make the Grignard reagent? Convert to an alkyl halide, if necessary. •Step #1: React alkyl halide with Mg in ether to make Grignard Reagent. •Step #2: React Grignard reagent with an aldehyde, ketone, ester, or epoxide. •Step #3: Acid/base neutralization. Grignard Example #1 (ketone 3o alcohol) (3o alcohol) Grignard Example #2 (aldehyde 2o alcohol) (2o alcohol) Grignard Example #3 (ester 3o alcohol) (3o alcohol) Grignard Example #4 (epoxide 1o, 2o, or 3o alcohol) R=R’=H (1o alcohol) R=H, R’=alkyl (2o alcohol) R=R’=alkyl (3o alcohol)