Chemistry 331: Organic Chemistry Fall 2014, University of Delaware Prof. Donald Watson
advertisement

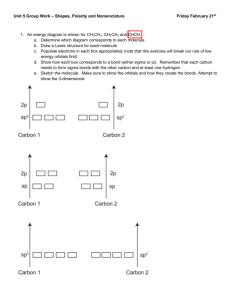
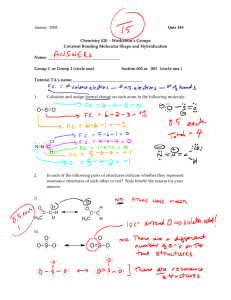
Chemistry 331: Organic Chemistry Fall 2014, University of Delaware Prof. Donald Watson Problem Set 1 Due Beginning of Class 9/12/14 You may work in groups. Please write answers in the space below, for problems form the book, please attached them on separate sheet(s) of paper. Each student must turn in their own, handwritten answer set to get credit. Please write answers on this page. Book problems: 1.48-1.51, 1.54, 1.59, 1.60 1. Write the electron configuration for the following elements: a. Lithium b. Nitrogen c. Phosphorus 2. What is the hybridization state of the methyl cation (CH3+) and the methyl anion (CH3-)? 3. Draw the molecular orbital diagram of H2. 4. Give the hybridization state of each carbon in the following molecule and mark them as primary, secondary, or tertiary. 5. Identify the orbital overlaps involved in the single bond of propene (CH2=CHCH3). Is this a π-bond or a σ-bond? 6. Consider the molecule hydrogen fluoride (HF). Draw the molecule and label the dipole moment. Which atom has more electron density? 7. Consider a carbonyl group (Carbon-oxygen double bond; C=O). Draw the molecular orbitals involved in the bonding interaction. Draw the dipole moment. Which atom has more electron density? Label the HOMO and LUMO. 8. Draw the resonance forms of the carbonate ion (CO32-) and use arrows to show the movement of electrons. 9. What is the bond angle of the four C-H bonds in methane (CH4)? 10. What is the hybridization state of the nitrogen atom in ammonia (NH3)? 11. Draw all constitutional isomers of the following: a. C5H12 b. C3H8O 12. Draw the Lewis Dot structure for the following. (a) H2O2 (b) CH2O (c) HCN (d) NH2– CH3CO2– (e) HCO3– (f) 13. Draw an orbital picture of allene, H2C=C=CH2. Label the hybridization of all of the carbons. What shape do you predict for allene? 14. Draw a detailed picture of the hybrid orbitals involved in the bonding in propyne. 15. Draw a three-dimensional representation for each molecule. Indicate which have a dipole moment and in what direction it is pointing. (a) CH3F (b) CH2Cl2 (c) CH2ClBr (d) CHCl3 (e) 16. Isothiocyanates are versatile reagents in syntheses. There are three important resonance forms for methyl isothiocyanate (CH3NCS) in which all the atoms have closed shells and formal charges of -1, 0 or +1. (a) Draw these three resonance contributors. (b) Which of the three forms that you drew is the most important contributor to the actual structure of methyl isothiocyanate? Why? (c) Draw a picture of the most important resonance contributor of methyl isothiocyanate showing σ bonds, and indicating which p orbitals interact to give π bonds.