pKa's. H O DMSO
advertisement

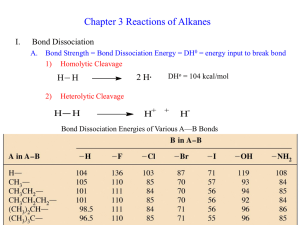
J. M. Ready UT Southwestern Valuable Numbers pKa's. Numbers are approximations for outside the range -2 - 16, but useful to know. For an extensive list, see http://www.chem.wisc.edu/areas/reich/pkatable/ H2O DMSO H2O DMSO Substrate Substrate Inorganics CF3SO3H -14 HCl CH3SO3H -8 H3O+ -2 NH4Cl 9 O O O O 9 13 11 14 13 EtO OEt 10 NO2-CH3 16 EtO 16 Organic X-H H + O Ph O 2 -3 H2O EWG-CH O O -6 CH3 20 27 25 30 O Me2OH+ AcOH NH+ PhOH O N H 17 H -4 5 12 5 3 10 18 15 26 t-BuO O Me2N 35 O S 33 Hydrocarbons H MeOH 16 28 tBuOH 17 29 (iPr)2NH 38 R H 98 H 103 H 125 H H H H Bond Strength. Take from Lowry and Richardson; by definition, ΔH for: Bond 44 H 41 BDE (Kcal/mol) 50 H3C 36 NH3 35 Bond 23 35 A + A B BDE (Kcal/mol) OH 84 O 172 (2nd bond = 88) B 85 81 Cl 82 Br 69 I 54 HO H HO2 H 119 90 HO OH 50 104 2-10 H H Hydrogen bond X H 148 (2nd bond = 67) 194 (3rd bond = 46) for a large list of BDE's see Prof. Thomas Lectka's web page: http://www.jhu.edu/chem/lectka/Bond%20Strengths.html Strain energy (energetic penalty for indicated strain) H3C Strain CH3 H Penalty (kcal/mol) ring strain 0.8 gauche H H H H3C CH3 eclipsed CH3 CH3 or O or O 28 26 2.2 H H H H Penalty (kcal/mol) Strain 6 syn-pentane 3.7 0 olefin conformations H3 C CH3 for CH3 H H3 C H3C H CH3 6 A1,2 2.7 H H3C H CH3CH3 A1,3 3.9 Kinetics and Thermodynamics equilibrium processes key equation: ∆G = -RTLn(K) for K = 10, T = 298, ∆G = -1.4kcal K = 100, T = 298 ∆G = -2.8kcal i.e. for every 1.4kcal difference in energy there is an order of magnitude change in Keq reaction rate 2nd key equation kBT −∆G‡ exp k= h RT or ∆G‡ = -RTLn kh kBT for T = 298, k = 1s-1 ∆G‡ = 17.5 kcal/mol i.e. activation energy for rxn occuring once a second is 17.5 As above, if k = 10s-1, ∆G‡ = 17.5 - 1.4 = 16.1 k = rate constant h = Plank's constant kb = Boltzmann's constant −∆G‡ = free energy difference between ground state and transition state For T = 308 and ∆G‡ = 17.5, k = 2.5s-1 i.e. increase in temp of 10K gives ~2.5 fold increase in rate relative rates for a system with 2 possible reaction pathways (e.g. kinetic enolization or asymmetric catalysis) for kfast/kslow = 10 (would give 82% ee), ∆∆G‡ = 1.4kcal/mol kfast/kslow = 100 (would give 99% ee), ∆∆G‡ = 2.8kcal/mol Bond distances length (angstroms [10-10m]) bond OH 1.43 O 1.23 1.53 1.34 1.20 H 1.1 H3 C H H3 C O X H (hydrogen bond) 0.97 1.5 - 2.4