CH 334 First Midterm Exam FORM_B Monday, October 18, 2010
advertisement

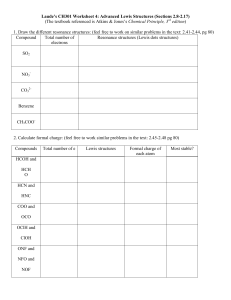
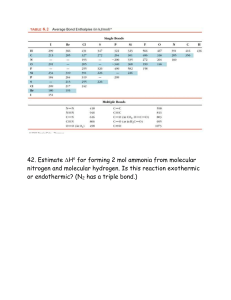
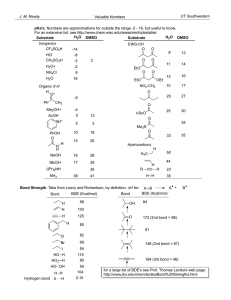
CH 334 First Midterm Exam FORM_B Monday, October 18, 2010 Name:____________________________________________________________ You may use molecular model kits but no other material with chemical information on it. Please do not use MP3 players or other electronic gadgets. Useful information: Table 3.6: X F CN Cl Br OH COOH CH3 CH2CH3 CH(CH3)2 C(CH3)3 -K, kJ/mol 0.8 0.8 2.1 2.5 4.1 5.9 7.6 7.9 8.8 23 1. (15 points) Draw correct Lewis structures (show all lone pairs) for the following compounds. a. (CH3)3NO b. C2H6O (any isomer) c. CH3CHO 2. (15 points) Draw the major resonance forms for the following molecule. Indicate which atom(s) will be Lewis basic. 4 points per structure; minor errors (missing charges): -2 pts Oxygens each have lone pairs in one or more resonance forms and should be Lewis basic; the carbonyl oxygen more than the one in the ring (3 points total) 3. (10 points) Label the hybridization of each carbon in the molecule shown below. 4. (5 points) Select the most accurate statement about rotating about the C2-C3 bond of butane. _____a. It is not possible to rotate about a bond. __X_b. Rotation about a bond is usually a low-energy process because there is no change in the overlap of the constituent hybrid atomic orbitals that make the bond. _____c. Because this breaks a bond, this process will have a very high energy barrier (in the hundreds of kJ/mol). _____d. There is a strict directional preference for clockwise rotation because of how the hydrogens interact. 5. (5 points) Select the most accurate statement about rotating about the C2-C3 bond in 2-methyl-2-butene. _____a. It is not possible to rotate about a bond. _____b. Rotation about a bond is usually a low-energy process because there is no change in the overlap of the constituent hybrid atomic orbitals that make the bond. _X__c. Because this breaks a bond, this process will have a very high energy barrier (in the hundreds of kJ/mol). _____d. There is a strict directional preference for clockwise rotation because of how the hydrogens interact. 6. (5 points) Consider the following resonance structures and select the most accurate statement about them. _____a. Presence of an electron deficient atom in some of these structures means there will be no resonance. _____b. These structures illustrate motion of electrons in the molecule as a function of time. _____c. The second structure is not a valid Lewis structure. __X_d. The actual distribution of electrons is shared among all carbon atoms. 7. (10 points). Name the following compounds. 3-methyloctane cis-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane 8. (10 points) Draw the following compounds from the names. a. 3-ethyl-2-methylpentane b. trans-1,2diethylcyclopentane 9. (25 points) The potential energy diagram for ring flip isomerism of trans1,4-dimethylcyclohexane is shown below. a. Assign the structures on the right hand side to the 5 points labeled with arrows in the diagram. 3 pts each; not necessary to distinguish D/E so long as they are each correctly identified as higher energy than A/B (E has a pseudoaxial methyl and should be higher energy). b. Explain why there is an energy difference between the two chair forms. 10 points. Structure B has two axial methyl groups. Each has steric compression with two axial hydrogens, so the energy cost for placing them axial should be about twice that for a single methyl group (Table 3.6: 2 x 7.6 kJ/mol = 15.2 kJ/mol). That it's a little more indicates that the molecule cannot deform as much to accommodate the strain when both sides experience the same steric compression. This detail is not necessary to answer the basic point of the question.