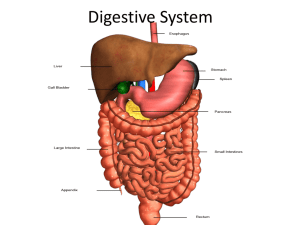
Biology 2402 The Digestive System Purpose:
advertisement

Biology 2402 The Digestive System Purpose: This lab will identify the structures of the digestive system and study the histology of selected structures. I. Anatomy of the Digestive System A. Identify the organs and structures of the alimentary canal B. Identify the structures of the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas II. Histology A. Identify the layers and associated structures in the model of a crosssection of the small intestine B. Identify the structures in models of the liver and pancreas In addition to the general goals above, specific anatomical structures that the student must be able to identify are listed below. A few select structures may be added to the list at the discretion of the instructor. WCJC Biology 2402 Rev 082110 PAGE 16 The Digestive System Description Page MAJOR STRUCTURES I. Oral Cavity A. tongue B. salivary glands 1. parotid gland 2. submandibular gland 3. sublingual gland C. dentition 1. central incisors 2. lateral incisors 3. canines 4. premolars/bicuspids 5. molars (1st, 2nd, 3rd) D. hard palate 1. palatine process of maxillae 2. palatine bone E. soft palate 1. uvula 137 143 II. Pharynx (also see p. 14 of handouts) A. oropharynx B. nasopharynx C. laryngopharynx 137 III. Esophagus 136 lower esophageal sphincter (cardiac sphincter or cardio-esophageal sphincter) IV. Stomach A. regions 1 cardiac region 2. fundus 3. body 4. pylorus B. other structures 1. greater curvature 2. lesser curvature 3. pyloric sphincter 4. rugae C. muscularis externa 1. longitudinal layer 2. circular layer 3. oblique layer WCJC Biology 2402 138 Rev 082210 PAGE 17 The Digestive System Description V. Small Intestine A. regions 1. duodenum a. duodenal papilla b. plica circularis 2. jejunum 3. ileum a. ileocecal valve B. mesentery VI. Large Intestine A. cecum 1. vermiform appendix B. colon 1. ascending colon a. right colic (hepatic) flexure 2. transverse colon a. left colic (splenic) flexure 3. descending colon 4. sigmoid colon C. rectum 1. anal canal 2. anus D. other structures 1. greater omentum 2. haustra 3. teniae coli Page 136, 139, 142-143 136, 139, 142 VII. Liver A. lobes: 1. right lobe 2. left lobe 3. caudate lobe 4. quadrate lobe B. blood entry and exit: 1. hepatic artery 2. portal vein 3. hepatic vein 4. inferior vena cava C. biliary tree: 1. gall bladder 2. right and left hepatic ducts 3. common hepatic duct 4. cystic duct 5. common bile duct 114, 136, 139, 143 WCJC Biology 2402 Rev 082210 --- -- PAGE 18 The Digestive System Description Page D. other structures 1. falciform ligament 2. round ligament -- VIII. Pancreas A. regions 1. head 2. body 3. tail B. major structures 1. main pancreatic duct 2. sphincter of hepatopancreatic ampulla (sphincter of Oddi) 136, 143 HISTOLOGY I. X.S. of Small Intestine A. mucosa (mucous membrane) 1. lamina propria 2. muscularis mucosae 3. epithelium (simple columnar) 4. villus a. capillary of villus b. lacteal of villus c. Intestinal crypt (crypt of Leiberkuhn) B. submucosa 1. Peyer's patches 2. Brunner's gland C. muscularis externa 1. longitudinal muscles 2. circular muscles D. serosa (visceral peritoneum) 140 II. Model of Liver Tissue branch of portal vein branch of hepatic artery bile duct sinusoids central veins bile canaliculi hepatocytes lymphatic vessels WCJC Biology 2402 144 -- Rev 082210 PAGE 19 The Digestive System Description Page -- III. Model of Pancreatic Tissue ductal cells - exocrine acinar cells - exocrine islets of Langerhans - endocrine IV. Slides A. pancreas 1. islets of Langerhans 2. acinar cells B. liver 1. hepatic lobule 2. central vein 3. hepatocytes 4. sinusoids WCJC Biology 2402 -- 144 Rev 082210 PAGE 20