Digestive System: Anatomy, Function & Process
advertisement
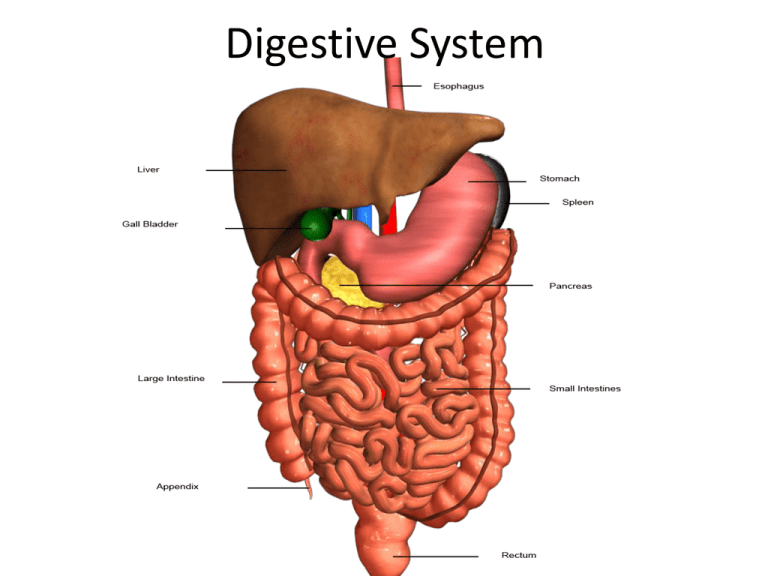
Digestive System • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_QYwscA LNng A.K.A • “GI” System • Alimentary or digestive tract Functions • Carries food for digestion • Prepares food for absorption • Transporting waste for elimination “The journey” • Begins in the mouth – Broken down mechanically and chemically • Mastication-chewing • Digestive enzymes-speed up chemical reaction • Proteins amino acids; complex sugarssimple sugars; large fat moleculesfatty acids, triglycerides – Absorption • Blood stream • Walls of small intestine – Fatty acids and triglycerides are absorbed in the small intestine – Elimination • Solid waste, passed from body • Feces collects in large bowel and exits through the anus Mouth “Oral cavity” • Hard palate- roof of the mouth • Muscular soft palate – Posterior to hard palate – Separates mouth from throat • • • • • • • • Pharynx Rugae-irregular ridges Uvula-aids in production of sound and speech Tongue (mastication, deglutition) Tonsils (lymphocytes) Gums Teeth-32 permanent Three pairs of salivary glands-produces saliva, containing digestive enzymes – Parotid, submandibular and sublingual Pharynx • Muscular tube • Passageway for food and air • Epiglottis-prevents food from entering trachea Esophagus • Pharynxstomach • Aids in swallowing • Peristalsis-involuntary contraction moving food through GI tract Stomach • • • • Fundus-top portion Body-middle portion Antrum-lower portion Sphincters – Cardiac, esophagusstomach – Pyloric, allows food to exit • Rugae-irregular ridges Small Intestine • • • • Pyloric sphincter large intestine 20 feet long Villi-microscopic projections; aid in digestion Three parts – Duodenum • • • • 1 foot long “12 inch” Receives food from stomach Receives bile from liver and gallbladder Receives pancreatic juice from pancreas – Jejunum • 8 feet long • Connects with 3rd section • “empty” – Ileum • 11 feet long • Attaches to large intestine • “to roll” Large Intestine • Ileum anus • Four parts – Cecum • Right side connected by ileocecal sphinter • Vermiform appendix hangs from cecum – Colon • 5 feet long • 3 divisions – Ascending colon, cecum undersurface of liver – Transverse colon, horiz. To spleen then turns down – Descending colon, downward portion • Sigmoid colon • Rectum Liver • Located in RUQ • Bile – Emulsification-breaking apart of fat globules so pancreas can digest • Continuously released from liver • Functions – – – – – Keep glucose levels normal Removes excess glucose, glycogenesis Converts glycogen into glucose Converts proteins and fats into glucose, gluconeogenesis Removal of poisons from the blood Gallbladder • Under liver • Stores and concentrates bile for later use Pancreas • Exocrine gland • Produces amylase and lipase-enzymes that aid in digestion • Secretes insulin – Insulin is needed to release sugar from the blood to be used by cells in the body Digestive System Diagram 4/21 Assignment! • Pgs. 484-486 Combining forms (write in your notes) • Check abbreviations with the textbook











