8th Grade Vocab Section 1: Matter Physical Properties: properties
advertisement

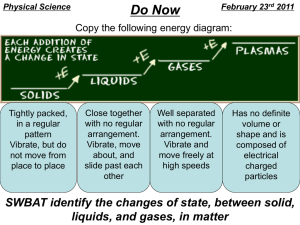
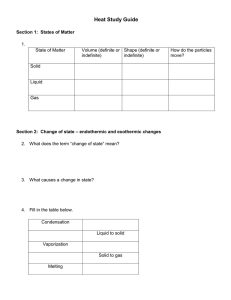
8th Grade Vocab Section 1: Matter Physical Properties: properties that can be observed without changing the identity of the substance Chemical Properties: properties describing how a substance changes into something new Physical Change: the change of a substance in which the identity of said substance remains the same Chemical Change/Reaction: The change of a substance into a new and different substance Melting Point: the point at which a solid changes to a liquid Freezing Point: the point at which a liquid changes to a solid Boiling Point: the point at which a liquid changes to a gas Phase Changes: adding or removing energy to result in a change of volume, but not of mass Sublimation: solid gas Deposition: gas solid Vaporization: liquid gas (boiling) Evaporation: liquid gas (stagnant) Melting: solid liquid Freezing: liquid solid Condensation: gas liquid Density: the amount of mass in a given volume of matter (D = M / V) Mass: The amount of matter in an object Matter: Anything that takes up Space or has mass Volume: the amount of space an object takes up (L x W x H OR Displacement Method) Flammability: the ability of matter to burn Reactivity: the ability of matter to combine chemically with other substances Oxidation: reaction involving Oxygen that happens slowly Combustion: reaction involving oxygen that happens violently (explosions/burning) Corrosion: rusting Energy: The ability to cause changes in matter Kinetic Energy: the energy of moving matter Temperature: the amount of heat present in (or absent from) an object (Also called “Heat Energy” Reactants: What exists before a chemical reaction occurs Products: what exists after a chemical reaction occurs Chemical equation: the way to represent chemical reactions using a formula with Reactants on the left and products on the right Reaction Rate: Whether a reaction occurs quickly or slowly Concentration: the number of particles of a substance in a given volume. Catalyst: substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction. Surface Area: the amount of matter exposed to and able to react with another substance in a reaction Law of Conservation of Mass: Matter cannot be created or destroyed in chemical reactions Law of Motion: An object in Motion will stay in motion, an object at rest will stay at rest, unless acted upon by an outside force Antoine Lavoisier: Scientist who made the Law of Conservation of Mass 8th Grade Vocab Section 1: Matter Physical Properties: Chemical Properties: Physical Change: Chemical Change/Reaction: Melting Point: Freezing Point: Boiling Point: Phase Changes: Sublimation: Deposition: Vaporization: Evaporation: Melting: Freezing: Condensation: Density: Mass: Matter: Volume: Flammability: Reactivity: Oxidation: Combustion: Corrosion: Energy: Kinetic Energy: Temperature: Reactants: Products: Chemical equation: Reaction Rate: Concentration: Catalyst: Surface Area: Law of Conservation of Mass: Law of Motion: Antoine Lavoisier: