cell test review key
advertisement

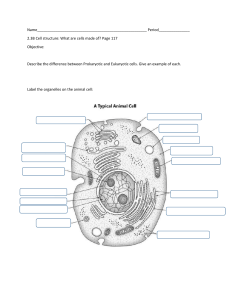
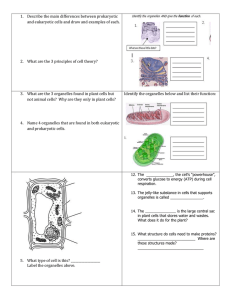
Name___________________________________________ Cell Test Review Using the diagram of a cell above, name the structure and give the function for that structure in the space below: Number Name of Organelle Function of Organelle endoplasmic reticulum moves proteins around cell 1 2 3 4 5 nucleus holds DNA and controls cell mitochondria creates ATP for energy cell membrane controls movement into and out of cell; surrounds cell golgi apparatus packages and transports proteins out of cell or around cell 1. Is the cell above a plant or an animal cell? animal cell How can you tell? no cell wall; no chloroplasts Using the diagram of a cell to the left, answer the following questions (name and number from the diagram): 7. Which structure regulates what comes into and goes out of the cell? number 3 (cell membrane) 8. Which structure is the site where amino acids are synthesized into proteins? number 2 (ribosomes) 9. Which structure is the place where ATP is made in the cell? number 1 (mitochondria) 10. Which structure stores the genetic information? number 4 (nucleus) 11. In the space below, explain the difference between a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell in terms of size, organelles and number of cells prokaryotic cells are smaller than eukaryotic cells; prokaryotic cells don’t have organelles or a nucleus 12. In the space below, explain the difference between plant and animal cells in terms of organelles and shape: plant cells are a more defined shape because they have a cell wall; they have a central vacuole for water storage and chloroplasts for photosynthesis 13. Why are cells small? they need to be small to move things more easily throughout the cell; they need to maintain a large surface area to volume ratio 14. What happens to the surface-area-to-volume ratio as a cell gets larger? as the cell get larger, the surface area to volume ratio gets smaller 15. Define organelle: smallest part of a cell; performs a certain function 16. Organize the following terms in order of levels of organization smallest to largest: Tissue Cells Organs Atoms Organelles Biomolecules Compounds Organ Systems atoms, compounds, biomolecules, organelles, cells, tissue, organs, organ systems 17. In the space below, explain the difference between a virus and a bacterium. a virus only contains DNA; 18. Define Pathogen: disease causing substance 19. Define Parasite: organisms or virus that benefits from a relationship by harming a host 20. Why is a virus considered a parasite? it benefits from its host and the host is harmed 21. Do we consider viruses to be alive? Why or why not? No or we don’t know because they don’t possess all the characteristics of life. For example, they reproduce, but they can’t control their own homeostasis. They evolve, but they aren’t made of cells. 22. Describe how a virus infects its host: attaches to host cell and inserts genetic material; the genetic material is used to create various virus parts which are then assembled into a virus that bursts out of the host cell 23. Describe the structure of a virus: capsid (protein coat that protects DNA), genetic material (can be DNA or RNA), spikes (to help attach to host cell) 24. List the 3 parts of the cell theory: 1) all living things are made from one or more cells 2) the cell is the basic unit of structure and function for all organisms 3) all cells come from other cells 25. If the magnification on the ocular lens of a microscope is 10X and the magnification on the objective lens is 40X, what is the total magnification? ocular lens X objective lens 10X x 40X = 400X magnification 26. Define diffusion: movement of solute across the cell membrane from high to low concentration 27. Define osmosis: diffusion of water across the cell membrane from high to low concentration 28. In what direction do solute and water normally move? high to low concentration 29. What is the difference between passive and active transport? (in terms of energy and direction of movement) passive transport moves from high to low concentration and doesn’t use energy active transport moves from low to high concentration and uses energy 30. Draw a picture to illustrate the following things: (Be sure to show where the most solute is located and use arrows to show which direction water will move.) Hypertonic solution water exits cell Hypotonic solution water enters cell Isotonic solution water moves in and out of cell at equal rates