Describe the main differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic
advertisement

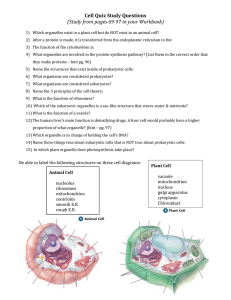
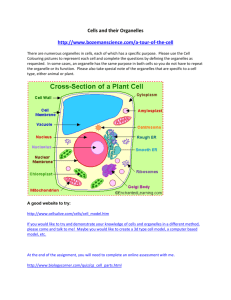
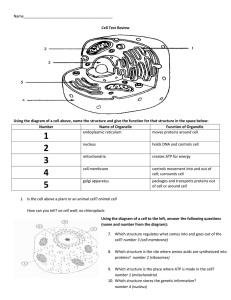
1. Describe the main differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and draw and examples of each. 2. What are the 3 principles of cell theory? 3. What are the 3 organelles found in plant cells but not animal cells? Why are they only in plant cells? Identify the organelles below and list their function: 4. Name 4 organelles that are found in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. 12. The _____________, the cell’s “powerhouse”, converts glucose to energy (ATP) during cell respiration. 13. The jelly-like substance in cells that supports organelles is called ________________. 14. The _______________ is the large central sac in plant cells that stores water and wastes. What does it do for the plant? 15. What structure do cells need to make proteins? ____________________________ Where are these structures made? ________________________________ 5. What type of cell is this? ___________________ Label the organelles above. 16. In which organelle does DNA replication take place in order for new cells to have a copy of DNA? _________________________________ Why is DNA important? 17. Name the 2 structures that are found in animal cells and not found in plant cells. _______________________ and _____________________________________. 18. What is the FUNCTION of the cell/plasma membrane? 6. What type of cell is this? ___________________ Label the organelles above. 19. What type of cell needs the most mitochondria? (nerve, muscle, blood, or bacteria) Why? 20. Smooth ER makes and transports lipids for the cell membrane; however, it also contains many enzymes for detoxifying chemicals. Knowing this, what type of cells would have a lot of smooth ER? (nerve, muscle, liver, or heart) Why? 21. Your mouth is the first place chemical digestion 7. What type of cell is this? ___________________ Label the organelles above. begins to break down your food. What organelle do you think is found in your mouth that helps with this task? Why?