File
advertisement

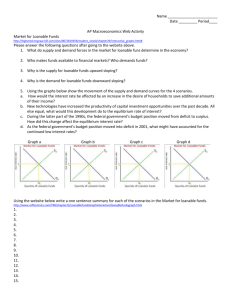
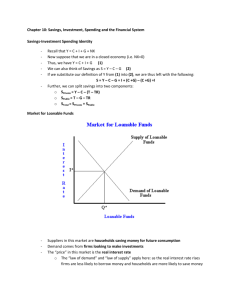
Chapter 26: Savings, Investment Spending and the Financial System – 1 A Hole in the Ground – What is the function of the financial system? What are the benefits of the system? ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ Matching up Saving and Investment Spending – What is the difference between investment spending and making an investment? How are they related? ___________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ The Savings-Investment Identity – It is a fact that savings and investment spending are always _______________. In your own words, explain why savings must equal investment spending in a closed economy with no government. ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ When the government spends less than it collects, there is a budget __________________. In this case, there is positive government ___________________. When government savings and private savings are added together, the sum is called _____________________ savings. Since our government doesn’t usually save, it _____________ spends, government savings is usually a ____________________ number. If the government doesn’t save and the people do not save enough, the U.S. can rely on investment in our economy by ____________________________. This amount – inflow of funds from foreigners minus outflow of funds to foreigners – is called _________________ _________________. In the U.S. this number is generally positive, while in China it is generally ______________. Why are capital inflows a less desirable source of funds for domestic investment spending? ___________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ There are three main types of capital in economics. In this chapter, we are dealing mainly with ________________ capital as the source of funding for the other two - _____________________ and ____________________ capital. How does U.S. private savings compare with the rest of the world? _____________________________________ Why? ___________________________________________________________________ How is this low rate of savings possible? ______________________________________________________________________________ (FIM, p. 678) How does the accounting for ‘unsold inventory’ help make it certain that savings equals investment? ____________________________________________________________________________________________ p. 700, problem 1. (Tip: T = total taxes collected) investment spending = ________ private savings = _____ budget balance = ________ Relationship between 3: _________________________________ Does I = S? ____ 2. I = ___________ PS = ____________ budget balance = ___________ KI = _______________ Relationship among 4: _________________________________________________________________________ 3. Capsland budget balance = _______ Marsalia budget balance = _______ Which has a deficit? __________ 4. a. PS = ________ (show work here) c. Budget balance = _________ b. I = ________ d. IM – X =________ The Market for Loanable Funds – The _______________________ markets bring savers and borrowers together. While there are many different financial products available that have different risks and rates of return, we will simplify the financial markets into one market called the ___________________ ________________ market. In this market there is only one __________________ _____________ (r), represented on the y-axis. All savings are represented on the x-axis as the ______________________ of ____________________ _______________. Define the term ‘rate of return’ in describing why the demand for loanable funds is a downward sloping curve. ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ Why is the supply of loanable funds curve upward sloping? _____________________________________________ Which curve, S or D, represents Investment spending (I)? ____ Which curve represents Total Savings (TS)? ____ How does the loanable funds market create efficient outcomes? _________________________________________ ____________________________________ Note that firm belief in this market distinguishes western economies. For example, China is more leery about private risk assessment by banks that may require a government bailout. Shifts of the Demand for Loanable Funds – Describe how each will lead to a shift in the demand curve: Changes in perceived business opportunities: _______________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ Changes in government borrowing: _______________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ EXTREMELY IMPORTANT POINT: When the government borrows more, which it does when it ________ spends, interest rates in the whole economy ____________. This will push the interest rates above the rates of return on certain investment projects. This decrease in I slows the economy since I is a component of _________. When more G means less I, the effect is referred to as ____________________ ___________. The government, which does not seek profit and is generally less efficient, has crowded out the growth-seeking ___________ sector. Shifts of the Supply of Loanable Funds - Changes in private savings behavior: ____________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ Changes in capital inflows: ______________________________________________________________________ Inflation and Interest Rates – While S of and D for loanable funds are important in determining r, perhaps the most important factor historically is the expected future _________________ rate. When inflation is expected to be high, _________________ interest rates will be high. As long as inflation is expected, the __________ interest rate does not change even as the nominal interest rate does. This is known as the ____________________ effect. Figure 26-8 shows us that r can be affected by both ________________ and ______________________________. Chapter 26: Savings, Investment Spending and the Financial System – 2 CYU 26-1 1.a. b. 2. _________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. a. ______________________________ b. ___________________________ c. ________________________ Pr 6.a. 7. New r = ______ b. New Q =______ c. Any crowding out? __________________________________ 8. Diagram a & b here. c. ________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ 10. _________________________________________________________________________________________ 11. a. ________________________________________________________________________________________ b. __________________________________________________________________________________________ 12. _________________________________________________________________________________________ The Financial System – Define the following terms and put them in context in the financial system. Wealth _____________________________________________________________________________________ Financial asset _______________________________________________________________________________ Physical asset - _______________________________________________________________________________ Liability ____________________________________________________________________________________ Three Tasks of the Financial System – How does the financial system do each of the following: Reduce transaction costs? _______________________________________________________________________ Reduce risk through diversification? ______________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ Provide liquidity? _____________________________________________________________________________ Types of Financial Assets – What are the advantages and disadvantages of each of the following assets? Loans - _____________________________________________________________________________________ Bonds - _____________________________________________________________________________________ Loan-Backed Securities - _______________________________________________________________________ Stocks - _____________________________________________________________________________________ Financial Intermediaries – What service do each of the following provide, and what issue do they resolve? Mutual Funds _______________________________________________________________________________ Pension Funds and Life Insurance Cos. - __________________________________________________________ Banks - _____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ CYU 26-2, 1. a-c. Fill in table ranking each asset on the measures listed. Asset Bank deposit w/ guaranteed interest rate Share of highly diversified mutual fund, can be quickly sold Share of family business, can be sold to willing buyer w/ family approval Tr. Costs Risk Liquidity 2. __________________________________________________________________________________________ Pr. 14. a. _______________ b. _______________ c. _______________ d. _______________ e. _______________ Financial Fluctuations – How can fluctuations create severe short-terms stress on financial markets? ____________________________________________________________________________________________ The Demand for Stocks and Other Assets – How do each of the following affect the valuation of stocks? Investors’ beliefs about future value ______________________________________________________________ Attractiveness of substitute assets _______________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ Asset Price Expectations – What is the efficient markets hypothesis, and how might it involve a random walk? ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ In what ways are markets sometimes irrational? How does this detract from the efficient markets hypothesis? ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ Asset Prices and Macroeconomics – Why do macroeconomists want to believe in the efficient markets hypothesis? ____________________________________________________________________________________________ Describe the two events in recent U.S. history that support the idea that markets are often irrational and macro-economists should be concerned with over-valuation. _________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ Pr. 17. a. ____________________ b. ____________________ c. ____________________ d. __________________ 18. a. ________________________________________________________________________________________ b. ____________________ c. ____________________________________________________________________