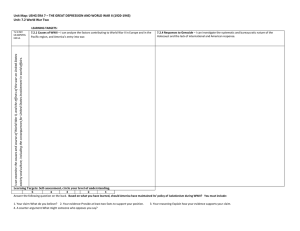
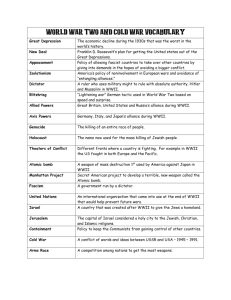
7 th Grade US History SOL Review Packet
advertisement
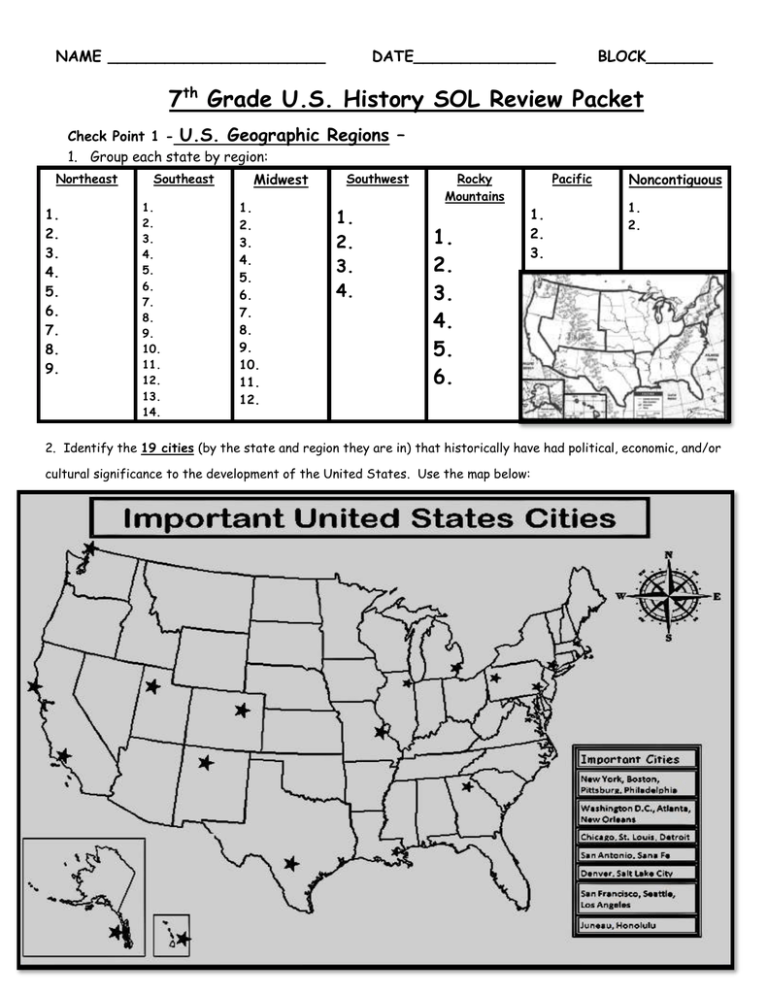
NAME _______________________ DATE_______________ BLOCK_______ 7th Grade U.S. History SOL Review Packet Check Point 1 - U.S. Geographic 1. Group each state by region: Northeast 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Southeast 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Midwest 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Regions – Southwest 1. 2. 3. 4. Rocky Mountains 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Pacific 1. 2. 3. Noncontiguous 1. 2. 2. Identify the 19 cities (by the state and region they are in) that historically have had political, economic, and/or cultural significance to the development of the United States. Use the map below: U.S. Civil War Reconstruction – 1. Fill –in-the blank: The 13th, 14th, & 15th Amendments to the Constitution of the United States of America guarantee __________ _____________ ____________ _____ _________ for all citizens. 2. What are the basic provisions of the 13th, 14th, and 15th Amendments to the Constitution of the United States? In other words, what rights and freedoms do these amendments protect? 13th _____________________________________________________________________ 14th _____________________________________________________________________ 15th _____________________________________________________________________ 3. What were the Reconstruction policies for the South? __________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. What were some of the problems the South faced because of the harsh Reconstruction policies created by the North?_____________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 5. What were the lasting impacts of the actions of the following three Reconstruction leaders? Abraham Lincoln: ___________________________________________________________ Robert E. Lee: _____________________________________________________________ Frederick Douglass: _________________________________________________________ 6. What is racial segregation?________________________________________________________ 7. What were “Jim Crow” laws? 8. What African-American believed social equality could be achieved through vocational education and accepted “social segregation?” _______________________ 9. What African-American believed in full political, civil, and social rights for all African-Americans? _____________________ Check Point 2 – U.S. Western Expansion– 1. Fill-in-the-Blank: How did people’s perceptions and use of the Great Plains change after the Civil War? Because of new ______________________ , people saw the Great Plains not as a “____________________________” but as a vast area to be ____________________. 3. Describe what the physical features and climate of the Great Plains were like. _________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Technological advances allowed people to live in more challenging environments. List the inventions and adaptions that allowed people to adapt to life in the challenging environment of the plains.___________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 5. How did advances in transportation link resources, products, and markets?_____________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 6. What are three examples of manufacturing areas that were located near centers of population? *______________(New England) *_______________(Detroit) *______________(Pittsburgh) 7. Why did westward expansion occur after the Civil War? (List 5 reasons)_____________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 8. How where the lives of American Indians impacted by western expansion?_____________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 9. Describe who the following Native Americans were and how they dealt with “Westward Expansion.” Sitting Bull:_______________________________________________________________ Chief Joseph of the Nez Percé:________________________________________________ Geronimo:_______________________________________________________________ 10. What effect did the reduction of the buffalo population have on the Native Americans?__________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 11. What happened at the “Battle of Wounded Knee?”_____________________________________ U.S. Immigration and Population Growth– 1. Fill-in-the-Blank: ______________________ changes, ________________ of cities, and new ____________ produced interaction & often conflict between different ____________ groups & in urban areas. 2. Why did immigration increase during the industrialization era?_____________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. Why did cities grow & develop during the late 1800s & early 1900s?__________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. What two groups of immigrants were most often discriminated against? _____________________ 5. What challenges faced Americans as a result of these social & technological changes? ____________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 6. Who was Jane Addams & what did she create? ________________________________________ Check Point 3- The U.S. Progressive and Industrialization Era: 1. Fill-in-the-Blank: Between the ___________________ and ________________________, the United States was transformed from an ___________________ to an ______________________ nation. 2. _____________________ had both __________________ and __________________ effects on society. 3. What 2 inventions and inventors created great change and industrial growth in the United States? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. What created the rise and prosperity of big business during the Progressive Era? _______________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 5. Name the 3 top “captains of industry” and the “big business” they created during the Progressive Era. ________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 6. What factors caused the growth of industry during the Progressive Era?______________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 7. How did industrialization and the rise in big business influence life on American farms? ___________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 8. How did the reforms of the Progressive Movement change the United States?__________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 9. What were some of the negative effects of this time era and how did American workers and the public respond to the negative effects of industrialization?__________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 10. What major union formed as a result of the “rise in organized labor?” _______________________ 11. What was the name of the plant where a violent steal strike occurred in Pennsylvania? __________ 12. List some of the workplace reforms the individuals of the “Progressive Movement” wanted.________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 13. What was the main goal of the “Woman’s Suffrage Movement?”___________________________ 14. Name the founders of the “Woman’s Suffrage Movement?”_______________________________ 15. What amendment finally gave women the right to vote? __________________________________ 16. What were the main goals of the “Temperance Movement?”_______________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ The Age of Invention: 1. What were the results of improved transportation and more affordable automobiles?_____________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 2. Who invented the airplane?________________________________ 3. How did communication change in the late 1800s and early 1900s? ____________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. Who used the assembly line to increase factory and labor productivity? ________________________ Check Point 4 -The Spanish American War 1. What were the reasons for the Spanish American War? ___________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. What were the results of the Spanish American War?_______________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ 3. What did Theodore Roosevelt’s Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine state? ________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ 4. What was the United States able to build in Central America as a result of Theodore Roosevelt’s “big Stick” Diplomacy? _________________________________________ World War I: 1. What were the 4 reasons for the United States’ becoming involved in World War I? _____________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 2. List the major Allied Powers. ______________________________________________________ 3. List the major Central Powers? _____________________________________________________ 4. The United States provided international leadership at the conclusion of the war by introducing President Woodrow Wilson’s 14 Points during the Versailles Treaty. What was the name of the peacekeeping organization introduced, but never joined, by the U.S.? ____________________________ The Roaring 20s and the Great Depression: 1. What were some of the technologies that changed American life in the early 20th century?__________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 2. Who made popular the use of the moving assembly line? ___________________________________ 3. Who had an important role in the development of the radio? ________________________________ 4. What was Prohibition?_____________________________________________________________ 5. What were speakeasies? ___________________________________________________________ 6. What were bootleggers? ___________________________________________________________ 7. What was the Great Migration? ______________________________________________________ 8. What was the Harlem Renaissance? ___________________________________________________ 9. Who was a Harlem Renaissance painter who chronicled the experiences of the Great Migration north through art? ___________________________ 10. Who was a Harlem Renaissance poet who combined the experiences of African and American cultural roots?__________________________________ 11. Name two Harlem Renaissance jazz composers? _____________________ ___________________ 12. Who was a Harlem Renaissance blues singer? _________________________ 13. Which artist of the 1920s was known for urban scenes and paintings of the Southwest? ____________ 14. Who wrote novels about the Jazz Age of the 1920s? ___________ 15. Who wrote Grapes of Wrath, a novel about poor migrant worker during the 1930s? _____________ 16. Name 2 composers of the 1920s and 1930s who wrote uniquely American music?_______________ ____________________ 17. What were causes of the Great Depression? ____________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 18. The ___________ __________ failed to prevent the collapse of the banking system which triggered the Great Depression. 19. What were the major features of the New Deal? ________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ Check Point 5 - World War II 1. What were the conditions in Europe after World War I that led to the rise of fascism and WWII? _____________________________________________________________________________ 2. What is fascism? ______________________________________________________________ 3. America’s foreign policy during WWII was to remain “neutral,” but the U.S. got involved in Europe’s conflict by lending & leasing battleship & war materials to England. What this policy called? _________ 4. Which nations were known as the major Allies and their leaders? Country Leader Roosevelt/Truman Churchill 5. Which countries were ruled by fascist dictators and became known as the Axis Powers? Country Leader Germany Italy Japan 6. On September 1, 1939, Hitler invaded _____________. World War II had begun. 7. What event on Dec. 7, 1941 caused the United States to declare war on Japan?__________________ 8. What happened after the U.S. declared war on Japan after the bombing of Pearl Harbor?__________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 9. In June of 1940, German troops marched victoriously into this European capital. ____________, France 10. From August until October 1940, Germans bombed British cities, shipyards and industries. This was known as the___________________________. 11. What was the turning point in the war in the Pacific?___________________ 12. Where did the American and Allied troops land to begin the liberation of Western Europe? __________ 13. The Soviet Union defeated Germany at______________, marking the turning point of the war in Eastern Europe. 14. How did the US force Japan to surrender and bring an end to World War II? __________________ 15. Why did American involvement in WWII bring an end to the Depression? ______________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 16. As many as six million Jews died during the ____________________ 17. Nazi troops crammed Jews into railroad cars & took them to prison camps called _________________ 18. What is anti-Semitism and Aryan supremacy? ____________________________________________ 19. Many women had not worked before WWII. An advertising campaign which encouraged women to take factory jobs featured a character called ____________________________. 20. How did Americans support the war effort (WWII) at home? ______________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ Check Point 6 - POST WWII: 1. What parts of Europe did Soviet forces occupy after WWII? _______________________________ 2. What happened to Germany after WWII? _______________________________________________ 3. When and why was the United Nations established? ________________________________________ 4. What was America’s plan to rebuild Europe prevent the spread of communism called?________________ 5. What happened to Germany after WWII? ____________________________________________ 6. What country occupied Japan after WWII? __________________________________________ 7. Near the end of WWII, what was done to try to prevent future world wars? ____________________ 8. What happened to labor unions after WWII? ____________________________________________ 9. What changes occurred in the American workforce after WWII? _____________________________ 10. After WWII, women left the workforce and returned to their families. Did they stay out of the workforce? _________ 11. What was the result of the state of tension which developed between the two superpowers – the U.S. & the Soviet Union? _______________________ The Cold War Era: 1. The U.S. and the Soviet Union ideologically different. How? The U.S. was _________ and ___________. In contrast, the Soviet Union was ________________ and _______________. 2. What is “containment”? ___________________________________________________________ 3. Our allies in Europe formed a military alliance called _____________________________. 4. What caused the Korean conflict?______________________________________________________ 5. What was the Vietnam conflict? ______________________________________________________ 6. What was the Cuban Missile Crisis? ____________________________________________________ 7. What event signal became symbolic of the collapse of communism in Eastern Europe? ______________________________ 8. Changes in society after WWII included expanded educational & economic opportunities for _________. 9. One of the factors leading to changes in US society after WWII was a strong US economy which was the result of _______________________________. 10. When and what was “The Baby Boom”? __________________________________________________. 11. This president’s wife helped to helped to expand women’s rights. What was her name? ______________ 12. What gave educational, housing, and employment benefits to World War II veterans? ______________ 13. How did immigration change in the period after 1965? ____________________________________ Check Point 7 - The Civil Rights Era 1. Women activists were inspired by the achievements of the ______________________ and took action to gain equality, particularly in the workplace. 2. After World War II, women sought equality in the ___________________ . 3. What were some effects of segregation on American society?________________________________ 4. The Supreme Court decision in Plessy v. _____________ allowed schools and other facilities that were segregated by race. 5. Who called for passive resistance against segregated schools?_______________________________ 6. Rosa Park’s actions resulted in the _______________ bus boycott. 7. What does NAACP stand for? __________________________________________________ 8. Which laws supported the struggle for equality for African Americans? ________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 9. How were women disadvantaged in the workplace? ________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 10. What organization campaigned for women’s rights? ________________________________________ Globalization: 1. Which industries benefited the most from the new technologies of the second half of the twentieth century? ______________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 2. What impact did the new technologies of the twentieth century have on American life? ___________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 3. How has U.S. foreign policy changed since WWII and the Cold War? ___________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. Which two ethnic groups make up the largest percentage of immigrants to the U.S.? _______________ 5. What concerns does the U.S. have about our global environment? _____________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ Representative citizens have influenced America scientifically, culturally, academically, and economically—Name them. Science: Culture: Academics: Economics: -______________: Medicine (plasma) -________________: Architecture -________________: History -_________________: Physics (Manhattan Project team) -________________: Dance -________________: Literature -_______________: Computer technology (Microsoft) -________________: Franchising (McDonald’s) NAME __________________________ DATE___________ BLOCK_______ 7th Grade United States History SOL Review Packet U.S. Geographic Regions A state is an example of a political region. States may be grouped as part of different regions, depending upon the criteria used. Cities serve as centers of trade and have political, economic, and/or cultural significance. States grouped by region: Northeast: Maine, Vermont, New Hampshire, Connecticut, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania Southeast: Maryland, Delaware, West Virginia, Virginia, Kentucky, Tennessee, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, Florida, Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana, Arkansas Midwest: Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Michigan, Wisconsin, Minnesota, Iowa, Missouri, Kansas, Nebraska, South Dakota, North Dakota Southwest: Texas, Oklahoma, New Mexico, Arizona Rocky Mountains: Colorado, Utah, Nevada, Montana, Wyoming, Idaho Pacific: Washington, Oregon, California Noncontiguous: Alaska, Hawaii Cities: Northeast: New York, Boston, Pittsburgh, Philadelphia Southeast: Washington, D.C., Atlanta, New Orleans Midwest: Chicago, St. Louis, Detroit Southwest: San Antonio, Santa Fe Western (Rocky Mountains): Denver, Salt Lake City Pacific: San Francisco, Los Angeles, Seattle Noncontiguous: Juneau, Honolulu U.S. Civil War Reconstruction: Basic provisions of the U.S Constitutional Amendments: These 3 amendments guarantee equal protection under the law for all citizens. o The 13th Amendment bans slavery in the United States and all of its territories. o The 14th Amendment grants citizenship to all persons born in the United States and guarantees them equal protection under the law. o The 15th Amendment ensures all citizens the right to vote regardless of race, color, or previous condition of servitude. Reconstruction Policies: The Reconstruction policies were harsh and created problems in the South. Reconstruction attempted to give meaning to the freedom that former enslaved African Americans had achieved. -Reconstruction policies and problems: o Southern military leaders could not hold office. o African Americans could hold public office. o African Americans gained equal rights as a result of the Civil Rights Act of 1866, which also authorized the use of federal troops for its enforcement. o Northern soldiers supervised the South. o The Freedmen’s Bureau was established to aid former enslaved African Americans in the South. o Southerners resented Northern “carpetbaggers,” who took advantage of the South during Reconstruction. o Southern states adopted Black Codes to limit the economic and physical freedom of former slaves. End of Reconstruction: o Reconstruction ended in 1877 as a result of a compromise over the outcome of the election of 1876. o Federal troops were removed from the South. o Rights that African Americans had gained were lost through “Jim Crow” laws. Abraham Lincoln: Reconstruction plan calling for reconciliation Preservation of the Union was more important than punishing the South Robert E. Lee: Urged Southerners to reconcile with Northerners at the end of the war and reunite as Americans when some wanted to continue to fight Became president of Washington College, which is now known as Washington and Lee University Frederick Douglass: Fought for adoption of constitutional amendments that guaranteed voting rights Was a powerful voice for human rights and civil liberties for all African-Americans. Post-Reconstruction in the South. Discrimination against African Americans continued after Reconstruction. “Jim Crow” laws institutionalized a system of legal segregation. African Americans differed in their responses to discrimination and “Jim Crow.” Racial segregation o Based upon race o Directed primarily against African Americans, but other groups also were kept segregated o American Indians were not considered citizens until 1924. “Jim Crow” laws o Passed to discriminate against African Americans o Made discrimination practices legal in many communities and states o Were characterized by unequal opportunities in housing, work, education, and government African American Responses: o Booker T. Washington: Believed equality could be achieved through vocational education; accepted social segregation o W.E.B. DuBois: Believed in full political, civil, and social rights for African Americans. U.S. Western Expansion: During the nineteenth century, people’s perceptions and use of the Great Plains changed. Technological advances allowed people to live in more challenging environments. Because of new technologies, people saw the Great Plains not as a “treeless wasteland” but as a vast area to be settled. Physical features & climate of the Great Plains Flatlands that rise gradually from east to west Land eroded by wind and water Low rainfall Frequent dust storms Inventions and adaptations Barbed wire Steel plows Dry farming Sod houses Beef cattle raising Wheat farming Windmills Railroads Advances in transportation linked resources, products, and markets. Manufacturing areas were clustered near centers of population. Transportation resources: o Moving natural resources (e.g., copper, lead) to eastern factories o Moving iron ore deposits to sites of steel mills (e.g., Pittsburgh) o Transporting finished products to national markets Examples of manufacturing areas: o Textile industry: New England o Automobile industry: Detroit o Steel industry: Pittsburgh Reasons for increase westward expansion: Opportunities for land ownership Technological advances, including the Transcontinental Railroad Possibility of obtaining wealth, created by the discovery of gold and silver Desire for adventure Desire for a new beginning for former enslaved African Americans Impact on American Indians: Opposition by American Indians to westward expansion (Battle of Little Bighorn, Sitting Bull, Geronimo) Forced relocation from traditional lands to reservations (Chief Joseph, Nez Percé) Reduced population through warfare and disease (Battle of Wounded Knee) Assimilation attempts and lifestyle changes (e.g., reduction of buffalo population) Reduced their homelands through treaties that were broken U.S. Immigration and Population Growth: Population changes, growth of cities, & new inventions produced interaction & often conflict between different cultural groups and in urban areas. Reasons for the increase in immigration Hope for better opportunities Desire for religious freedom Escape from oppressive governments Desire for adventure Reasons why cities grew and developed: Specialized industries, including steel (Pittsburgh) and meat packing (Chicago) Immigration to America from other countries Movement of Americans from rural to urban areas for job opportunities Rapid industrialization and urbanization led to overcrowded immigrant neighborhoods and tenements. Efforts to solve immigration problems: Settlement houses, such as Hull House founded by Jane Addams Political machines that gained power by attending to the needs of new immigrants (e.g., jobs, housing) Discrimination against immigrants: Challenges faced by cities: Tenements and ghettos Political corruption (political machines) Chinese Irish The U.S. Progressive and Industrialization Era: Between the Civil War and World War I, the United States was transformed from an agricultural to an industrial nation. Inventions had both positive and negative effects on society. Inventions that contributed to great change and industrial growth: o Electric lighting and mechanical uses of electricity (Thomas Edison) o Telephone service (Alexander Graham Bell) Reasons for the rise and prosperity of big business: o National markets created by transportation advances o Captains of industry (John D. Rockefeller, oil; Andrew Carnegie, steel; Cornelius Vanderbilt, shipping and railroads) o Advertising o Lower-cost production Factors that resulted in growth of industry: Access to raw materials and energy Availability of work force due to immigration Inventions Financial resources Examples of big business: Railroads Oil Steel Postwar changes in farm and city life: Mechanization (e.g., the reaper) reduced farm labor needs and increased production. Industrial development in cities created increased labor needs. Industrialization provided new access to consumer goods (e.g., mail order). The Progressive Movement: The effects of industrialization led to the rise of organized labor and important workplace reforms. Negative effects of industrialization: Child labor Low wages, long hours Unsafe working conditions Rise of organized labor: Formation of unions: Growth of American Federation of Labor Strikes: Aftermath of Homestead Strike Progressive Movement workplace reforms: Improved safety conditions Reduced work hours Placed restrictions on child labor Women’s suffrage: Increased educational opportunities Attained voting rights Women gained the right to vote with passage of the 19th Amendment to the Constitution of the United States of America. Susan B. Anthony and Elizabeth Cady Stanton worked for women’s suffrage. Temperance movement: Composed of groups opposed to the making and consuming of alcohol Supported the 18th Amendment to the Constitution of the United States, prohibiting the manufacture, sale, and transport of alcoholic beverages. The Age of Invention: Technology extended progress into all areas of American life, including neglected rural areas. Results of improved transportation brought about by affordable automobiles: o Greater mobility o Creation of jobs o Growth of transportation-related industries (road construction, oil, steel, automobile) o Movement to suburban areas Invention of the airplane: o The Wright brothers Use of the assembly line: o Henry Ford, automobile o Rise of mechanization Communication changes: o Increased availability of telephones o Development of the radio and broadcast industry o Development of the movies Ways electrification changed American life: o Labor-saving products (e.g., washing machines, electric stoves, water pumps) o Electric lighting o Entertainment (e.g., radio) o Improved communications The Spanish American War: The United States emerged as a world power as a result of victory over Spain in the Spanish American War. Economic interests and public opinion often influence United States involvement in international affairs. Reasons for the Spanish American War: Protection of American business interests in Cuba American support of Cuban rebels to gain independence from Spain Rising tensions between Spain and the United States as a result of the sinking of the USS Maine in Havana Harbor Exaggerated news reports of events (yellow journalism) Results of the Spanish American War: The United States emerged as a world power. Cuba gained independence from Spain. The United States gained possession of the Philippines, Guam, and Puerto Rico Roosevelt expanded the Monroe Doctrine as a way to prevent European involvement in the affairs of Latin American countries. The Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine: o o o World War I: Asserted the United States’ right to interfere in the economic matters of other nations in the Americas. Claimed the United States’ right to exercise international police power Advocated Big Stick Diplomacy (building the Panama Canal). The United States’ involvement in World War I ended a long tradition of avoiding involvement in European conflicts and set the stage for the United States to emerge as a global superpower later in the twentieth century. There were disagreements about the extent to which the United States should participate in world affairs. Reasons for United States involvement in World War I: 1. 2. 3. 4. Inability to remain neutral. German submarine warfare: Sinking of the Lusitania. United States economic and political ties to Great Britain. The Zimmermann Telegram World War I Major Allied Powers: British Empire France Russia Serbia Belgium United States World War I Central Powers: German Empire Austro-Hungarian Empire Bulgaria Ottoman Empire United States leadership as the war ended: o At the end of World War I, President Woodrow Wilson prepared a peace plan known as the Fourteen Points that called for the formation of the League of Nations, a peacekeeping organization. o The United States decided not to join the League of Nations because the United States Senate failed to ratify the Treaty of Versailles. The Roaring 20s: Reforms in the early twentieth century could not legislate how all people behaved. Economic conditions and violence led to the migration of people. Prohibition was imposed by a constitutional amendment that made it illegal to manufacture, transport, & sell alcohol. Results of prohibition: Speakeasies were created as places for people to drink alcoholic beverages. Bootleggers made and smuggled alcohol illegally and promoted organized crime. Repealed by the 21st Amendment. Great Migration North and West: Jobs for African Americans in the South were scarce and low paying. African Americans faced discrimination and violence in the South. African Americans moved to cities in the North and Midwest in search of better employment opportunities. African Americans also faced discrimination and violence in the North and Midwest. 1920s and 1930s Music, Ligature and Art: The 1920s & 1930s were important decades for American art, literature, and music. The leaders of the Harlem Renaissance drew upon the heritage of African American culture to establish themselves as powerful forces for cultural change. Art: Literature: Music: Georgia O’Keeffe, an artist F. Scott Fitzgerald, a novelist who wrote about Aaron Copland and known for urban scenes and, the Jazz Age of the 1920s. George Gershwin, later, paintings of the Southwest. John Steinbeck, a novelist who portrayed the composers who wrote strength of poor migrant workers during the uniquely American 1930s. music. Harlem Renaissance: African American artists, writers, and musicians based in Harlem revealed the freshness and variety of African American culture. The popularity of these artists spread beyond Harlem to the rest of society. Art: Literature: Music: Jacob Lawrence, a painter who Langston Hughes, a poet who Duke Ellington and Louis chronicled the experiences of the Great combined the experiences of Armstrong, jazz musicians. Migration through art. African and American cultural Bessie Smith, a blues roots. singer. The Great Depression and Roosevelt’s New Deal: The optimism of the 1920s concealed problems in the American economic system and attitudes about the role of government in controlling the economy. The Great Depression had a widespread and severe impact on American life. Franklin Roosevelt’s New Deal used government programs to help the nation recover from the Depression. Causes of the Great Depression: Impact (Effects) on Americans: People over-speculated on stocks, using borrowed money that they could not repay when stock prices crashed. A large number of banks and other businesses failed. One-fourth of workers were without jobs. The Federal Reserve failed to prevent the collapse of the banking system. Large numbers of people were hungry and homeless. High tariffs discouraged international trade. Farmers’ incomes fell to low levels. Major features of the New Deal: Social Security Federal work programs Environmental improvement programs Farm assistance programs Increased rights for labor World War II: Political and economic conditions in Europe following World War I led to the rise of fascism and to World War II. The rise of fascism threatened peace in Europe and Asia. As conflict grew in Europe and Asia, American foreign policy evolved from neutrality to direct involvement. Causes of World War II: Political instability and economic devastation in Europe resulting from World War I: Worldwide depression High war debt owed by Germany High inflation Massive unemployment The Axis Powers Fascist dictators included: Adolf Hitler (Germany) Benito Mussolini (Italy) Hideki Tojo (Japan). Rise of Fascism: Fascism is political philosophy in which total power is given to a dictator and individual freedoms are denied and nationalism and, often, racism are emphasized. These dictators led the countries that became known as the Axis Powers. The Allied Powers Democratic nations included: Franklin D. Roosevelt and, later, Harry S. Truman (United States) Winston Churchill (Great Britain & Canada) A Socialist nation included: Joseph Stalin (Soviet Union). *The Soviet Union joined the Allies after being invaded by Germany. Gradual change in American policy from neutrality to direct involvement: Isolationism (Great Depression, legacy of World War I) Economic aid to Allies Direct involvement in the war War in the Pacific: Rising tension developed between the United States and Japan because of Japanese aggression in East Asia. On December 7, 1941, Japan attacked the United States at Pearl Harbor without warning. The United States declared war on Japan. Germany declared war on the United States. Despite initial Axis success in both Europe and the Pacific, the Allies persevered and ultimately defeated Germany and Japan. Major events and turning points of World War II: Germany invaded Poland, setting off war in Europe. The Soviet Union also invaded Poland and the Baltic nations. Germany invaded France and captured Paris. Germany bombed London, and the Battle of Britain began. The United States gave Britain war supplies and old naval warships in return for military bases in Bermuda and the Caribbean (Lend Lease). Japan bombed Pearl Harbor. After Japan bombed Pearl Harbor, Germany declared war on the United States. The United States declared war on Japan and Germany. The U.S. was victorious over Japan in the Battle of Midway. This victory was the turning point of the war in the Pacific. Germany invaded the Soviet Union. The S.U. defeated Germany at Stalingrad, marking the turning point of the war in Eastern Europe. American and other Allied troops landed in Normandy, France, on D-Day to begin the liberation of Western Europe. The United States dropped two atomic bombs on Japan (Hiroshima and Nagasaki) in 1945, forcing Japan to surrender & ending WWII. The Holocaust: The Holocaust is an example of prejudice and discrimination taken to the extreme. Tactics: Boycott of Jewish stores. Threats. Anti-Semitism Segregation. Aryan supremacy Imprisonment and killing of Jews and others in Systematic attempt to rid Europe of all Jews concentration camps and death camps. Those who survived in concentration camps were liberated by Allied forces. Effects of American involvement in World War II and the Home Front: World War II affected every aspect of American life. Americans were asked to make sacrifices in support of the war effort and the ideals for which Americans fought. o American involvement in World War II brought an end to the Great Depression. Factories and workers were needed to produce goods to win the war. o Thousands of American women took jobs in defense plants during the war (e.g., Rosie the Riveter). o Americans at home supported the war by conserving and rationing resources. o The need for workers temporarily broke down some racial barriers (e.g., hiring in defense plants), although discrimination against African Americans continued. o While many Japanese Americans served in the armed forces, others were treated with distrust and prejudice, and many were forced into internment camps. Post WWII: Learning from the mistakes of the past, the United States accepted its role as a world superpower, helping to rebuild Europe and Japan and taking the leading role in establishing the United Nations. Much of Europe was in ruins following World War II. Soviet forces occupied most of Eastern and Central Europe and the eastern portion of Germany. The U.S. felt it was in its best interest to help rebuild Europe and prevent political and economic instability. Rebuilding Efforts: The United States instituted George C. Marshall’s plan to rebuild Europe (the Marshall Plan), which provided massive financial aid to rebuild European economies and prevent the spread of communism. Germany was partitioned into East and West Germany. West Germany became democratic and resumed self-government after a few years of American, British, and French occupation. East Germany remained under the domination of the Soviet Union and did not adopt democratic institutions. Following its defeat, Japan was occupied by American forces. It soon adopted a democratic form of government, resumed selfgovernment, and became a strong ally of the United States. Establishment of the United Nations: The United Nations was formed near the end of World War II to create a body for the nations of the world to try to prevent future global wars. The Cold War: Following WWII, Americans prospered due to an expanding economy stimulated by America’s involvement in the war. Reasons for rapid growth of the American economy following World War II: With rationing of consumer goods over, businesses converted from production of war materials to consumer goods. Labor unions merged and became more powerful; workers gained new benefits and higher salaries. Americans purchased goods on credit. The work force shifted back to men, and most women returned full time to family responsibilities. As economic prosperity continued and technology boomed, the next generation of women entered the labor force in large numbers. Changing patterns in American society since the end of WWII changed the way most Americans lived and worked. Policies & programs expanding Factors leading to changing patterns in United States society: educational & employment opportunities: Strong economy (healthy job market, increased productivity, increased demand for American products). Greater investment in education. The “Baby Boom,” which led to changing demographics. Interstate highway system. Evolving role of women (expected to play a supporting role in the family while increasingly working outside the home). Role of Eleanor Roosevelt in expanding human rights. African Americans’ aspirations for equal opportunities. G.I. Bill of Rights gave educational, housing, and employment benefits to veterans. Truman desegregated the armed forces. Civil Rights legislation led to increased educational, economic, and political opportunities for women and minorities. Origins of the Cold War: The Cold War: The state of tension without actual fighting between the United States and the Soviet Union, which divided the world into two camps. Differences in goals and ideologies between the United States and the Soviet Union (the two superpowers). The United States was democratic and capitalist; the Soviet Union was dictatorial and communist. The Soviet Union’s domination over Eastern European countries. American policy of containment (to stop the spread of communism). North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) versus Warsaw Pact Major conflicts in the post-World War II era: The Korean Conflict (War): South Korea and the United States resisted Chinese and North Korean aggression. The conflict ended in a stalemate. The Cuban Missile Crisis: occurred when the Soviet Union placed missiles in Cuba. The Soviets removed the missiles in response to a U.S. blockade of Cuba. The Vietnam Conflict (War): The United States intervened to stop the spread of communism into South Vietnam (Domino Theory). Americans were divided over whether the United States should be involved militarily in Vietnam. The conflict ended in a cease-fire agreement in which U.S. troops withdrew. Collapse of communism in Europe: Breakup of the Soviet Union into independent countries. Destruction of the Berlin Wall. New challenges: Role of United States military intervention. (“World police”). Environmental challenges. Global issues, including trade, jobs, diseases, energy. The Civil Rights Movement and the Changing Role of Women: The Civil Rights Movement resulted in legislation that ensured constitutional rights to all U.S citizens regardless of race. Some effects of segregation: Separate educational facilities and resources for white and African Civil Rights Movement: Opposition to Plessy v. Ferguson: “Separate but equal.” Brown v. Board of Education: Desegregation of schools. Martin Luther King, Jr.: Passive resistance against segregated facilities; “I have a dream…” American students. Separate public facilities (e.g., restrooms, drinking fountains, restaurants). Social isolation of speech. Rosa Parks: Montgomery bus boycott. Organized protests, Freedom Riders, sit-ins, marches. Expansion of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP). Civil Rights Act of 1964. Voting Rights Act of 1965. races. Changing role of women: Women activists were inspired by the achievements of the Civil Rights Movement & took action to gain equality for women, particularly in the workplace. Improved conditions: Workplace disadvantages: National Organization for Women (NOW) Discrimination against women Federal legislation to force colleges to give women equal athletic opportunities in hiring practices. The Equal Rights Amendment, despite its failure, and a focus on equal opportunity Lower wages for women than employment created a wider range of options and advancement for women in business and for men doing the same job. public service. After the war, Americans turned their energies to the development of peacetime technologies. New technologies in communication, entertainment, and business have dramatically affected American life. Industries benefiting from new technologies: Airline industry (jet engine) Automobile industry and interstate highway system Entertainment and news media industries Exploration of space Computer industry Satellite systems, telecommunications (pagers, cell phones, television) Impact of new technologies on American life: Increased domestic and international travel for business and pleasure Greater access to news and other information Cheaper and more convenient means of communication Greater access to heating and air-conditioning improved the quality of life and encouraged population growth in certain areas of the country. Decreased regional variation resulting from nationwide access to the same entertainment and information provided by national television and radio programming, Internet services, and computer games. Internet Globalization: Between the end of WWII and the present, the world has been marked by an increase in globalization & interdependence. o o Globalization is the linking of nations through trade, information, technologies, and communication. Globalization involves increased integration of different societies. Impact of globalization on American life: Improvement of all communications (e.g., travel, telecommunications, Internet) Availability of a wide variety of foreign-made goods and services. Outsourcing of jobs. American foreign policy, immigration policies, energy policies, & environmental policies affect people both in the US & in other countries. Foreign policy: Immigration: Global environment: Other issues: Increase in terrorist activities. Conflicts in the Middle East. Changing immigration patterns (e.g., Hispanic Americans, Asian Americans). More people want to immigrate to the United States than are allowed by law. Changing relationships with nations. Policies to protect the environment. Global climate change. Conservation of water and other natural resources. Energy issues (dependence on foreign oil). World health issues (global pandemics). Representative citizens have influenced America scientifically, culturally, academically, and economically. Science: Culture: Academics: Economics: -Charles Drew: Medicine (plasma) -Frank Lloyd Wright: Architecture -Henry Louis Gates: History -Bill Gates: Computer technology (Microsoft) -J. Robert Oppenheimer: Physics (Manhattan Project team) -Maya Angelou: Literature -Martha Graham: Dance What’s Due Today? Check Points A Day B Day April 29 May 5 April 28 April 30 May 2 May 7 May 6 May 9 May 8 May 13 May 12 -Post WWII -The Cold War Era May 14 -Civil Rights -Globalization May 1 May 15 -Ray Kroc: Franchising (McDonald’s) -Geographic Regions -Reconstruction -U.S. Western Expansion -Immigration -Progressive and Industrialization Era -Age of Invention -Spanish American War -WWI -Roaring 20s and Great Depression -WWII The Entire Packet is Due Today! Check Point 1 Check Point 2 Check Point 3 Check Point 4 Check Point 5 Check Point 6 Check Point 7